Solution Guide
Guide on Various Solutions Offered by MLCCs with Dipped Radial Leads – Outline
As electronic components mounted on PCBs, surface mount devices (SMDs) supporting surface mount technology (SMT) are mainly used. In particular, multilayer ceramic chip capacitors (MLCCs), which are often used as main passive components, have significantly contributed to the reduction of the size and weight of electronic equipment. On the other hand, conventional ceramic capacitors with leads are also actively utilized in various applications that take advantage of their particular characteristics. Moreover, in recent years, MLCCs with dipped radial leads have been attracting attention as a solution that compensates for the weakness of SMD type capacitors in automotive applications where devices are used under severe conditions. To respond to these advanced market needs, TDK is now offering a new halogen-free series of MLCCs with dipped radial leads for applications that require high reliability, including automotive electrical equipment. This new series of capacitors is very effective as a countermeasure against acoustic noise, PCB deflection, and noise in DC motors.
Why Capacitors with Leads Are Attracting Attention Once Again
Leads Are Not a "White Elephant," But Offer Various Functions and Advantages
Generally, electronic devices with leads are considered to be products compatible with the mounting technologies from a decade ago. Admittedly, leads are regarded as a "white elephant" in terms of size reduction or space conservation. However, although having no leads is an advantage of SMDs, it is also their weakness at the same time. Because various features of devices with leads cannot be realized by SMDs, they have come to attract attention once again as an effective solution for the fundamental problems of SMDs.
Appearance and Structure of MLCCs with Dipped Radial Leads
An MLCC with dipped radial leads is a ceramic capacitor having a structure in which two lead wires are soldered to the external electrodes of the MLCC which is then resin-coated (Fig. 1). In addition to the features unique to an MLCC, it also has advantages such as the alleviation of mechanical and thermal stress through the lead wires and an insulation and moisture-shielding effect from the resin coating. Specific examples of solutions offered by MLCCs with dipped radial leads are introduced below.
Fig. 1: Appearance and structure of MLCCs with dipped radial leads (FG Series/FA Series)
Acoustic Noise Countermeasure
Dielectric ceramics used for ceramic capacitors demonstrate an electrostrictive effect. The outer shape changes slightly when voltage is applied. The application of AC voltage expands or contracts the capacitor element, which causes MLCCs that are soldered to a PCB to vibrate the PCB. This vibration can generate an audible buzzing noise, and the phenomenon is called "acoustic noise." In MLCCs with dipped radial leads, the effect of the expansion and contraction of the capacitor element is reduced by the leads, offering an effective solution to the acoustic noise problem of surface mounted MLCCs.
PCB Deflection Countermeasure
Cracking of the solder joints of MLCCs mounted on PCBs is a problem caused by deflection of the PCB due to mechanical or thermal stress. The leads of MLCCs with dipped radial leads effectively absorb stress caused by deflection of the PCB and prevent this flex cracking.
Replacement for Film Capacitors
TDK's MLCCs with dipped radial leads with C0G temperature characteristics satisfy the EIA code C0G, which is the most stringent code for Low-k (Class 1) capacitors. Thanks to their extremely small rate of capacitance change when DC bias voltage is applied and very flat temperature characteristics, they can replace film capacitors. In addition, since they are smaller than film capacitors, they are also very effective for size reduction and space conservation as well as use in places where there is a height limit.
Tolerance to High-Temperature Environments Including Engine Compartments
Automotive electronic devices are used in temperature environments that range from extreme cold to blisteringly hot. In particular, in devices such as electronic control units (ECUs) that are placed in engine compartments or very close to engines, capacitors are required to be guaranteed to operate under temperatures as high as 150°C. TDK's automotive grade FA Series with dipped radial leads comply with AEC-Q200 and offer a wide variety of products with NP0 and X8R temperature characteristics guaranteed to operate at a maximum temperature of 150°C.
*NP0 temperature characteristics (temperature coefficient of capacitance (TCC) 0±30ppm/°C in the temperature range from -55°C to 150°C), X8R temperature characteristics (TCC±15% in the temperature range from -55°C to +150°C)
Noise Countermeasures in Automotive DC Motors (1): Solutions Offered by MLCCs with Dipped Radial Leads
With the development of automotive electrical systems, including power windows and electric mirrors, modern automobiles can use over 100 small DC motors units. As these are brush type DC motors, noise is generated from the contact between the brush and commutator during motor rotation. Using MLCCs with dipped radial leads to suppress the noise is an excellent option because they can be connected securely and easily by soldering or swaging and do not take up much space. The ability to be used in locations where no PCB is used is a unique feature of MLCCs with dipped radial leads.
Noise Countermeasures for Automotive DC Motors (2): Solution Offered by a Combination with Ring Varistors
TDK suggests using a combination of ring varistors and MLCCs with dipped radial leads as an effective noise countermeasure for automotive motors. TDK has the advantage of manufacturing both ring varistors and MLCCs with dipped radial leads. We offer solutions that meet the demands of our customers through our extensive product lineup.
1. Acoustic noise solution
Superiority of MLCCs with dipped radial leads as a countermeasure against PCB acoustic noise
Acoustic noise of ceramic capacitors is caused by the electrostrictive effect of dielectric ceramics used as the capacitor elements. This phenomenon is more common in high-k (Class 2) capacitors using ferroelectrics.
The electrostrictive effect is also called the "inverse piezoelectric effect". The appearance of voltage in a material in response to the deformation of the outer shape caused by physical stress is called the "piezoelectric effect". On the contrary, the electrostrictive effect is the deformation of the outer shape in response to the application of voltage. Dielectric ceramics are polycrystalline bodies consisting of many fine dielectric crystals, with each crystal grain having a direction in which it can easily become electrically polarized. Although this direction varies between crystals, the crystal grains move to align their directions when voltage is applied. This causes the outer shape of the ceramics to change, and the ceramics repeatedly expand or contract when AC voltage is applied (Fig. 2). In MLCCs that are soldered to PCBs, the expansion and contraction of the capacitor element causes the PCB to vibrate, which may generate a continuous audible buzzing noise like that of a flat speaker.
Fig. 2: Cause of acoustic noise of ceramic capacitors and solutions offered by MLCCs with dipped radial leads
As the intensity level of actual acoustic noise varies, it is not apparent at the design stage. It often becomes evident for the first time at the stage of prototype PCB creation and a countermeasure becomes necessary in a short period of time before shipment. In such cases, replacing board mounted MLCCs with MLCCs with dipped radial leads can provide an extremely easy and effective solution, as the expansion and contraction of the capacitor element is absorbed by the leads.
Fig. 3 shows a comparison between the acoustic noise intensities of an SMD component and a component with leads using the same MLCC. It shows that acoustic noise is suppressed to lower levels at any frequency in the component with leads. Reduction of squealing at 3 kHz and 5 kHz, which are audible regions, is particularly significant.
Fig. 3: Comparison of the acoustic noise intensities of a board mounted MLCC and an MLCC with dipped radial leads
2. Solution to PCB deflection
Supports to MLCCs weak to tensile stress
Stress by deflection of the PCB may cause cracking at the solder joint of an SMD component (Fig. 4, left). Although dielectric ceramic used for the capacitor elements of MLCCs is resistant to compression stress, it is weak against tensile stress. Because of this, PCB bending stress at the mounting position can cause cracking of the capacitor element itself. Cracking of the capacitor element may lead to performance deterioration if an open failure (disconnection of the internal electrodes) occurs, and may generate heat, smoke or fire if a short failure (conduction of the internal electrodes) occurs. In addition, there are cases where open failures progress to short failures if the capacitors continue to be used.
In automotive electronic devices exposed to mechanical stress such as vibration or shock, or thermal stress due to severe temperature changes, replacement of MLCCs with MLCCs with dipped radial leads becomes an effective solution to the problem of PCB deflection. Since the lead wires absorb the PCB bending stress, the impact on the MLCC soldered to the lead wires is reduced (Fig. 4, right). In addition, MLCCs with dipped radial leads also maintain high reliability in electronic devices that frequently receive impacts caused by dropping, such as keyless entry or smart entry systems.
Fig. 4: How PCB bending stress is applied to an SMD component and a component with leads
3. Solution related to replacement of film capacitors
Superior characteristics realized in a notably-reduced space
TDK's MLCCs with dipped radial leads featuring C0G temperature characteristics satisfy the EIA code C0G (temperature coefficient of capacitance of 0 ± 30ppm/°C in the temperature range from -55 to 125°C), which is the most stringent code for temperature compensating capacitors, and have the following features.
- 《Features of MLCCs with dipped radial leads featuring C0G temperature characteristics》
- ●Achieve high capacitance while having C0G temperature characteristics
- ●Superior moisture-shielding property compared to film capacitors
- ●Temperature characteristics equivalent or superior to those of film capacitors
- ●DC bias characteristics with no voltage dependence
- ●No polarity
Owing to these features, MLCCs with dipped radial leads are extremely effective not only for automotive applications but also for use in locations where further size and space reduction is required or where there are height restrictions, such as bypass or smoothing capacitors for switching power supplies, snubber circuits, or PFC input filters (Fig. 5).
Fig. 5: Advantages achieved by replacing film capacitors with MLCCs with dipped radial leads
4. Countermeasures against noise in automotive DC motors (1) Solution offered by MLCCs with dipped radial leads
Mounted easily and securely in small spaces without using PCBs
Modern automobiles can use over 100 small DC motor units in devices such as power windows, electric mirrors, and wipers (Fig. 6) in order to enhance convenience or safety. Most of these motors are DC motors with brushes, and wide-band noise is generated from the contact of the brush and commutator during operation. A commutator is a device that switches current direction according to rotor rotation; at the moment the current is turned off, a large counter electromotive force is generated in the coil by self-induction and causes surge or noise. Therefore, if no countermeasure is implemented, it may negatively affect automotive electronic devices, such as by disturbing the radio each time the wipers are operated.
As a countermeasure against the noise in DC motors described above, capacitors or inductors are used. However, if PCBs are used for mounting SMD components, various problems such as space or cost issues, and reduction of the noise suppression effect due to wiring occur. On the other hand, components with leads may solve issues related to space or cost, as they can be mounted easily and securely by means of soldering or swaging without taking up much space. The ability to be used in locations where PCBs cannot be used is an advantage unique to components with leads.
In addition, motor units for the powertrain system and / or driving/steering system are increasingly being placed inside the engine compartment. Therefore, the need for electronic components that can withstand temperatures up to 150°C is increasing. TDK offers a lineup of various automotive grade products that can withstand temperatures up to 150°C, including MLCCs with dipped radial leads.
Fig. 6: Applications of small DC motors for automobiles
Fig. 7 shows an example of MLCCs with dipped radial leads mounted on a small DC motor. Two MLCCs with dipped radial leads are compactly soldered to a small brush holder. High reliability is especially required of automotive DC motors used under severe conditions, including high weather, moisture, vibration, and shock. Multilayer capacitors with leads that are coated with resin can provide a simple and effective solution that can fulfill such requirements.
Fig. 7: Capacitors for noise suppression in an automotive DC motor
5. Countermeasures against noise in automotive DC motors (2) Solution through combination with ring varistors
Clears the extremely stringent noise regulation CISPR25 Class 5
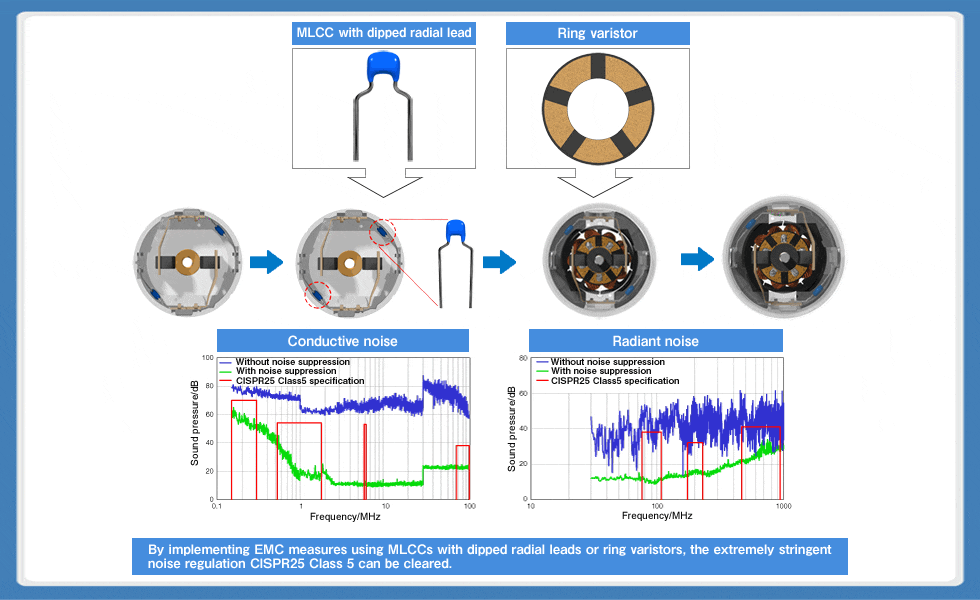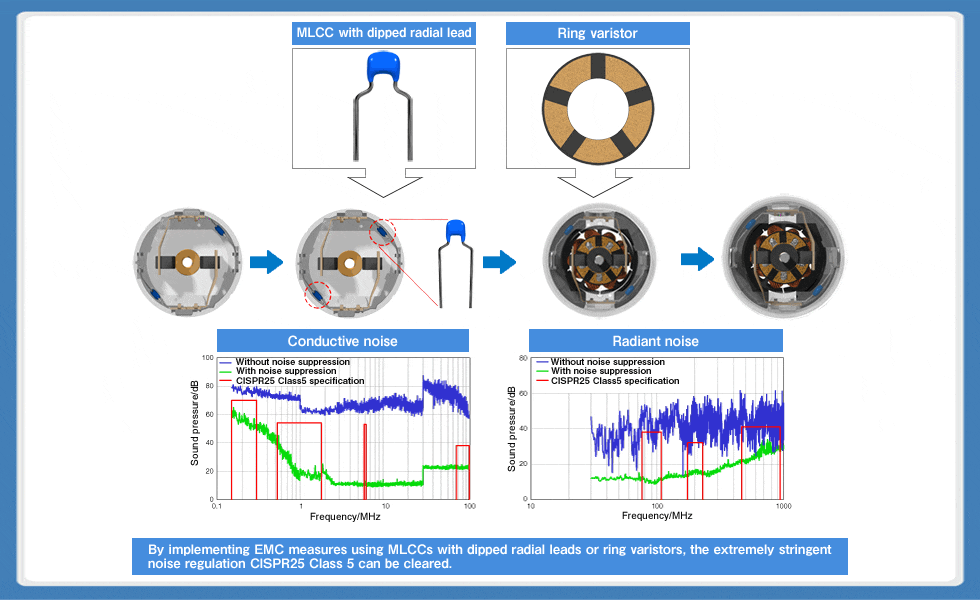
As a countermeasure against noise in DC motors with brushes, the effectiveness of MLCCs with dipped radial leads can be further enhanced by combining them with ring varistors. A varistor is a circuit protection element that uses a special semiconductor ceramic, and is mounted to protect electronic devices from ESD (electrostatic discharge), lightning surges and the like. A ring varistor is a ring-shaped component on whose surface electrodes with slits are attached and is used in conjunction with the commutators of DC motors. As a commutator rotates, large surge voltage is generated due to self-induction of the coil each time contact with the brush is lost. A ring varistor absorbs this surge voltage (Fig. 8).
TDK offers various types of ring varistors for small DC motors such as the VAR-18 series. By implementing noise countermeasures combining these ring varistors with MLCCs with dipped radial leads, compliance with CISPR25 Class 5, which is an extremely stringent international automobile EMC standard, can be achieved (Fig. 9).
Fig. 8: Structure and principle of ring varistors for DC motors
Click here for information on ring varistor products
Fig. 9: Solution for motors through the combination of MLCCs with dipped radial leads and ring varistors
Fig. 10 shows application examples of MLCCs with dipped radial leads and ring varistors in automotive DC motors. With 30-40mm as a threshold, ring varistors are used for smaller diameter motors, while MLCCs with dipped radial leads are used for larger motors. As it is expected that noise regulations for automobiles will become even more stringent in the future, the combination of MLCCs with dipped radial leads and ring varistors will be the noise solution for motors. One of TDK's strengths, as an electronic component and device manufacturer, is that it produces both ring varistors and MLCCs with dipped radial leads. We can promptly provide optimal solutions through our wide-ranging product lineup.
Fig. 10: Application examples of MLCCs with dipped radial leads and ring varistors
Click here for information on ring varistor products
With 30-40mm as a threshold, ring varistors are used for smaller diameter motors, while MLCCs with dipped radial leads are used for larger motors. By using them in combination, an excellent noise suppression effect can be achieved.
Guide on Various Solutions Offered by MLCCs with Dipped Radial Leads – Conclusion
An MLCC with dipped radial lead is a resin coated multilayered chip capacitor onto which lead wires have been soldered. Since the MLCC is covered with resin, it features a superior insulation property and moisture-shielding effect. Moreover, the structure with leads is highly effective in reducing mechanical and thermal stress, making the capacitor an optimum solution for acoustic noise and PCB deflection issues. In addition, since the capacitor can be mounted without a PCB by soldering or swaging, it realizes low-cost, space-saving noise suppression when used in the brush holder of a small automotive DC motor. When combined with a ring varistor, it becomes even more effective. Furthermore, MLCCs with dipped radial leads with C0G temperature characteristics featuring superior DC-bias characteristics or temperature characteristics can replace film capacitors while saving significant space. How about utilizing the features and characteristics unique to MLCCs with dipped radial leads in your products?
《Main features and applications of FG Series and FA Series of MLCCs with dipped radial leads》
【Main Features】
- Halogen-free
- Extensive product lineup
- General grade FG Series: Rated voltage 6.3V - 630V, capacitance 1pF - 100 μF
- Automotive grade FA Series: Rated voltage 25 V - 630 V, capacitance 100 pF - 22 μF
- Guaranteed operation at 150°C by products featuring the NP0 and X8R temperature characteristics,
enabling the products to withstand severe temperature environments - Automotive Grade FA Series is AEC-Q200 compliant
【Main Applications】
- Noise suppression in automotive DC motors
- Acoustic noise countermeasure
- PCB deflection countermeasure
- Resonance circuits in keyless entry systems, etc.
- Bypass or smoothing capacitors in switching power supplies, etc.
- Snubber circuits
- PFC input filters, etc.
Product Lineup: FG Series/FA Series MLCCs with dipped radial leads (as of May, 2016)
【MLCC with Dipped Radial leads】 Product Information and Sample Purchase
*Please select the grade, series and type suitable for your applications to improve the reliability of your products.