AMT45S: Compact, Reliable Pulse Transformer for xEV Charging


The Critical Role of Pulse Transformers in Electric Vehicle Charging Control Circuits
A variety of charging connector standards are adopted for electric vehicles worldwide. Notable examples include CCS (Combined Charging System), which is widely used across Europe, NACS (North American Charging Standard) prevalent in North America, as well as CHAdeMO and GB/T. Among these, both CCS and NACS utilize Power Line Communication (PLC) for control communication during the charging process.
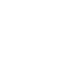
PLC enables the exchange of control signals between the vehicle and the charger via the charging cable. The charging system in electric vehicles typically consists of two main circuits: the power transmission circuit and the control circuit. The control circuit is responsible for managing the charging process with precision. Within this circuit, the pulse transformer plays a pivotal role by providing galvanic isolation against direct current, suppressing noise, and preserving signal integrity. The performance of the pulse transformer is directly linked to the reliability of charging control communication, overall charging efficiency, and battery performance, making it an indispensable component in the advancement of charging infrastructure.
Advantages of Next-Generation Pulse Transformers Over Conventional Designs
Currently, toroidal-type transformers are commonly used for PLC pulse transformers. However, traditional manufacturing processes such as manual winding make it challenging to ensure consistent winding time and stable product quality. Additionally, since PLC circuits superimpose communication signals onto power lines, pulse transformers are required to have high voltage resistance. As a result, many products feature resin coatings on the transformer section, which increases both size and cost.
The AMT45S utilizes advanced fully automated winding technology, enabling efficient production and stable quality for pulse transformers. For PLC circuits in xEV charging applications, high voltage resistance is not required, eliminating the need for resin coatings and allowing for a simpler, more compact product design. These advantages significantly enhance the flexibility of PCB design in electric vehicles and contribute to overall system cost optimization, making AMT45S a standout solution.
The table below compares conventional products with TDK’s new AMT45S model. By adopting automated winding technology, the AMT45S achieves substantial miniaturization, improved quality stability, and higher production efficiency compared to traditional products.
| Indicator | Market Product A | AMT45S | Reduction Rate / Improvement |
| Length [mm] Max | 11.4 | 4.7 | Approx. 59% |
| Width [mm] Max | 8.45 | 3.4 | Approx. 60% |
| Height [mm] Max | 8.5 | 3.0 | Approx. 65% |
| Volume [mm³] Max | Approx. 819 | Approx. 48 | Approx. 94% |
| Production Process | Manual winding, time-consuming | Automated winding, time-saving | Improved productivity |
| Quality Stability | Large variation | High stability | Significant improvement by automation |
Achieving Stable Insertion Loss Characteristics
PLC communication primarily operates at signal frequencies between 2MHz and 30MHz. To transmit and receive control information without degradation, pulse transformers with minimal signal waveform distortion at these frequencies are required. The AMT45S achieves miniaturization while delivering stable insertion loss (IL) characteristics across the 2MHz–30MHz range, thanks to high-quality automated winding and the selection of appropriate ferrite materials.
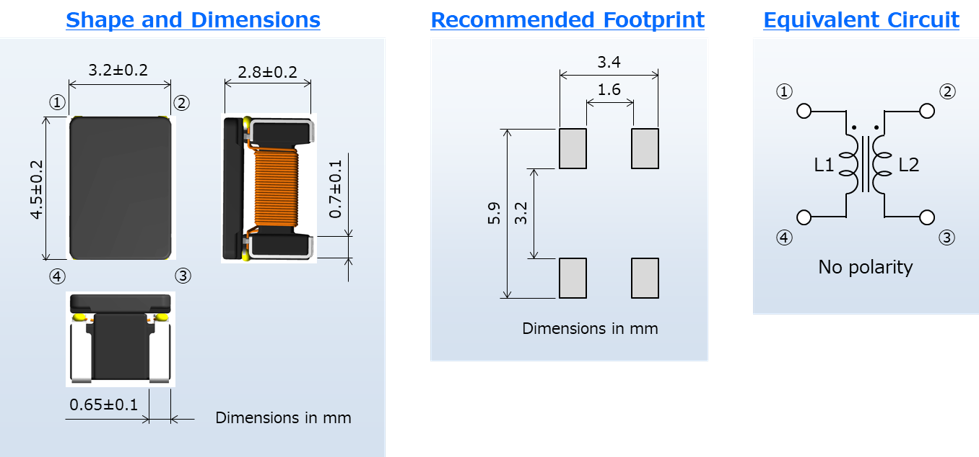
Product Design, Dimensions, and Equivalent Circuit
Please refer to the dedicated page below for more detailed specifications as well as product design, dimensions, and equivalent circuit.
Summary
As described above, the AMT45S achieves significant miniaturization compared to conventional products while ensuring excellent insertion loss (IL) characteristics required for xEV charging control circuits. In addition to the xEV charging infrastructure field, TDK will continue to pursue technological innovation and quality improvement, providing high-quality products to support society.
Download
Pulse Transformer AMT45S
Documentation

[FILE NAME]tdk-apn-trans-amt45s.pdf
[CAMPAIGN NAME]dm_t130_amt45s