Noise Countermeasures and Component Solutions for Automotive 48V Power Supply Systems

However, the higher voltage of automotive 48V power supply systems tends to increase noise levels, making noise control and EMC countermeasures more critical than ever. Insufficient EMC measures can lead to malfunctions and reduced reliability of automotive electronic devices, so effective noise control and EMC solutions are essential.
This solution guide introduces the latest examples of noise control and EMC countermeasures for automotive 48V power supply systems, featuring practical EMI suppression cases using our noise countermeasure components applied to DC/DC converters in automotive 48V power supply systems. If you are facing challenges with noise control or EMC solutions for automotive 48V power supply systems, we invite you to refer to this guide.
Background and Evolution of Automotive 48V Power Supply Systems
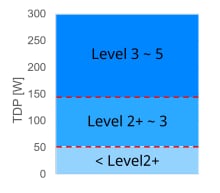
TDP of SoC used in ADAS/AD (TDK Assumption)
TDP: Thermal Design Power
(Maximum Heat Generation in Design)
With the widespread adoption of Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) and Autonomous Driving (AD), the automotive industry is rapidly advancing in the integration of high-performance SoCs (System on Chip) and AI functionalities.
As a result, the power consumption of automotive electronic devices is increasing. Traditional 12V power supply systems are facing challenges such as increased wire harness weight and overall vehicle weight due to higher current, as well as greater power loss. These issues negatively impact driving range and energy efficiency.
To address these challenges, the transition to automotive 48V power supply systems is accelerating. By adopting a 48V power supply, the same amount of power can be delivered with only one-fourth the current, enabling lighter wire harnesses, reduced power loss, and overall vehicle weight reduction. Therefore, automotive 48V power supply systems are gaining attention as essential technology for the electrification, higher efficiency, and extended driving range of next-generation vehicles.
Challenges Associated with Automotive 48V Power Supply Implementation
Increased Noise (EMC) Risk
Higher voltage leads to elevated levels of switching and conducted noise, requiring more stringent noise and EMC countermeasures than ever before.
Complexity in Component Selection and Design
48V-compatible components must have higher voltage ratings. Additionally, suppressing both common-mode and normal-mode noise necessitates multi-stage filters and the combination of high-performance components.
Ensuring System-wide Safety and Reliability
With 48V, the risk to human safety increases, making short-circuit, overcurrent, and overvoltage protection essential. It is necessary to balance EMC and safety measures to maintain overall vehicle reliability.
Impact on Cost and Space
The adoption of high-voltage components and multi-stage filters can increase component costs and PCB space requirements. However, benefits such as lighter wire harnesses and reduced wiring costs must also be considered, making balanced system design crucial.
Importance of Noise Control Measures in Automotive 48V Power Supply Systems
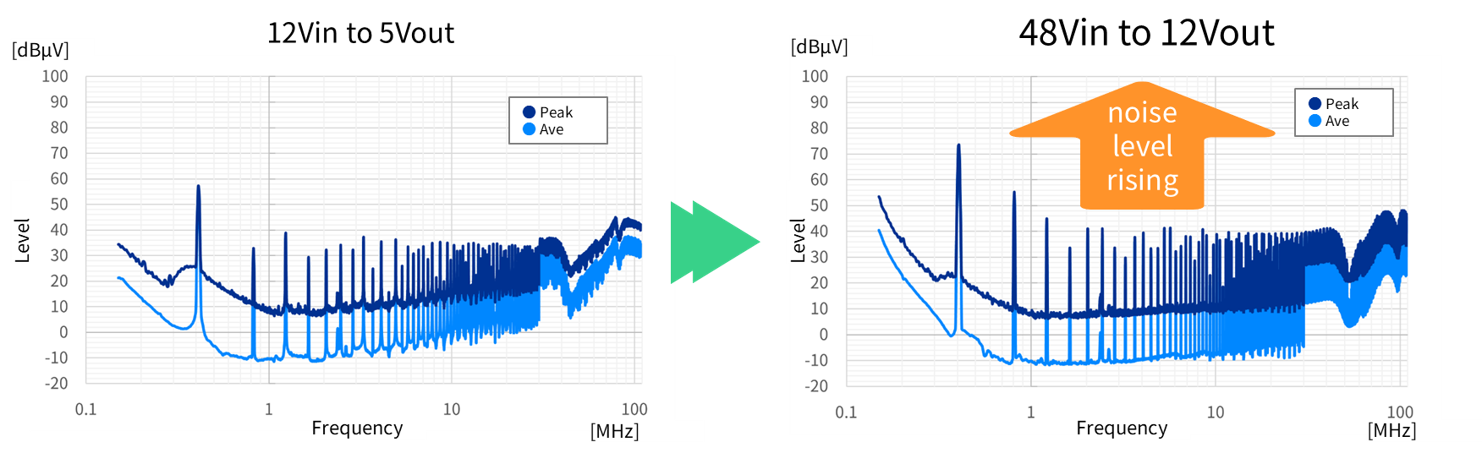
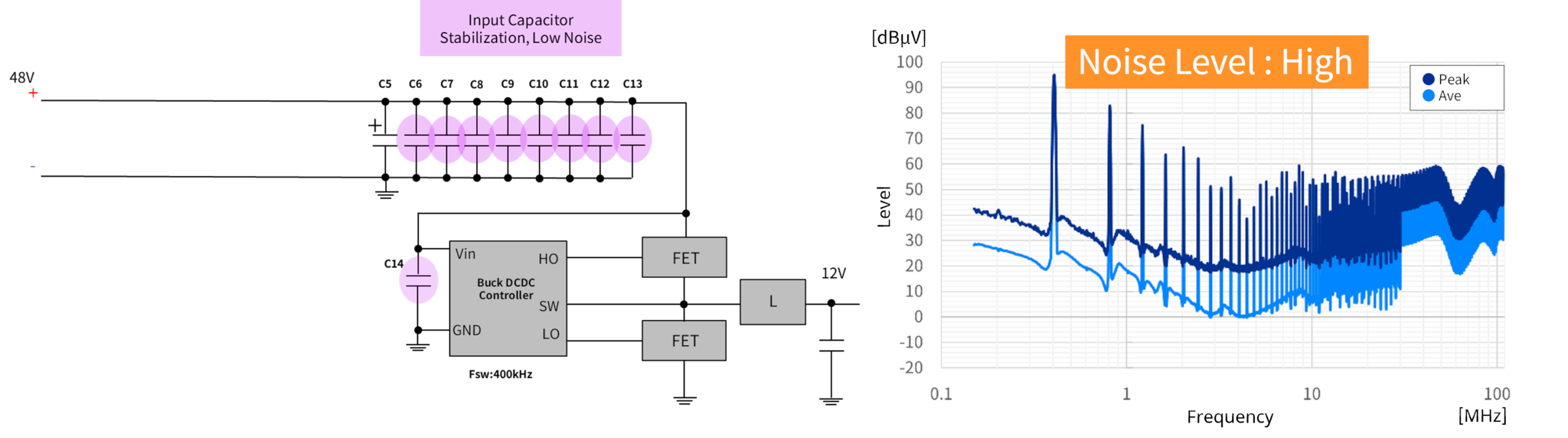
A comparison of conducted noise (measured by voltage method) using a DC/DC converter compatible with both 12V and 48V automotive power systems revealed that, even with the same board and component configuration, the 48V system generates higher noise levels than the 12V system (see Figure 1). This is because the higher input voltage of the 48V system increases the switching energy, amplifying noise components. The difference in noise levels is particularly pronounced across a wide frequency range from low to high frequencies, making EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility) countermeasures a critical issue for the entire automotive system, including 48V power supplies. Therefore, implementing noise filters and optimal noise control solutions is essential for automotive 48V power supply systems.
Selection of Noise Control Filter Components for Automotive 48V Power Supply Systems
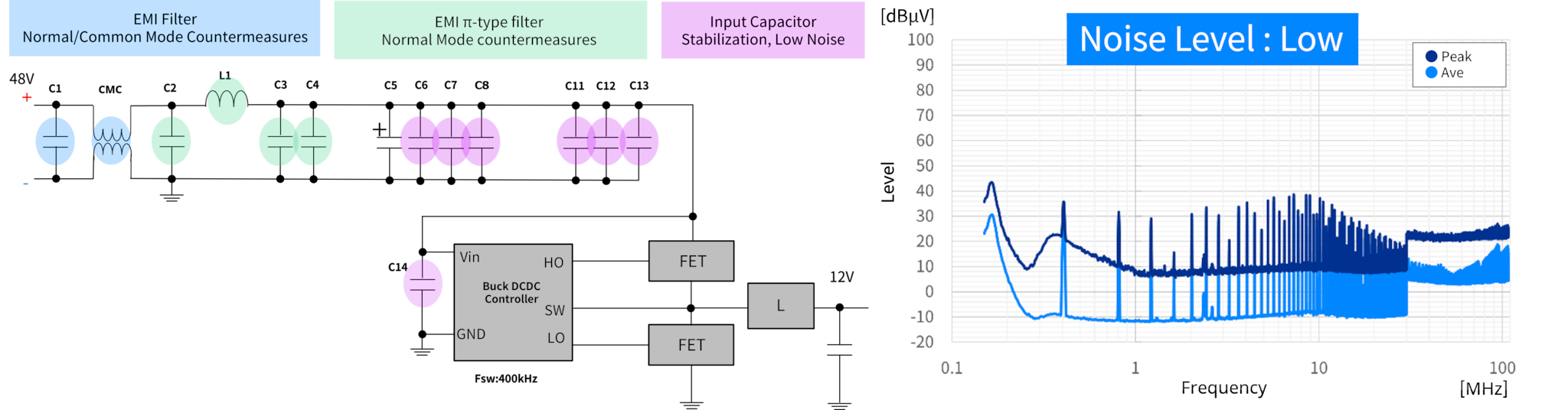
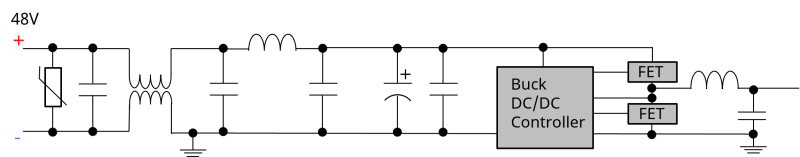
Figure 2 shows an example of noise control filter implementation in an automotive 48V power supply system. Since noise increases in 48V systems compared to 12V, multi-stage filters that address both common-mode and normal-mode noise are effective.
Table 1 summarizes the various filters and solutions, highlighting that optimal filter selection enhances the reliability and EMC performance of automotive 48V power supply systems.
| EMI Filter - Normal/Common Mode Countermeasures | EMI π-type filter - Normal Mode Countermeasures | Input Capacitor - Stabilization, Low Noise | ||||
| Contents | With the adoption of 48V systems, the parasitic capacitance between circuits increases, making higher common-mode noise more likely compared to 12V systems. Therefore, noise suppression using dedicated filters with common mode choke coils (CMC) is essential. Additionally, adding X capacitors at the input stage as a normal-mode countermeasure further enhances noise reduction. | A low-pass π-type filter effectively suppresses normal-mode noise caused by switching in power ICs and parasitic components. By combining capacitors and inductors, it attenuates a wide range of noise frequencies from low to high. | By combining large-capacitance and small-capacitance MLCCs, voltage line stabilization and reduction of input ripple voltage can be achieved. Using MLCCs with low impedance characteristics over a wide temperature range is highly effective. | |||
| Main Components Solutions | MLCC | MLCC | MLCC | |||
Power Line | Powe Line | |||||
Measured Examples of Noise Control Effectiveness in Automotive 48V Power Supply Systems
Using a commercially available DC/DC converter, the noise suppression effect with and without filters was verified. Input voltage and load conditions were set, and conducted noise (voltage method) was compared between filter-equipped and non-equipped setups to evaluate effectiveness.
Figure 3: Conducted Noise Voltage Measurement Environment
■ DC/DC Converter Conditions
Input Voltage: 48V
Output Voltage: 12V
Switching frequency: 400kHz
Output current: 7.2A
■ Measurement Environment
Measurement place: 3m Anechoic Chamber
Frequency : 150kHz-108MHz
■ Measurement Item
Conducted noise (voltage method)
■Measurement Results
| ■Without Filter | ||
| EMI Filter | EMI π-type filter | Input Capacitor |
| - | - | C6-C10: CGA6M3X7S2A475K200AB |
| - | - | C11-C14: CGA3E2X7R2A103K080AA |
| ■With Filter | |||
| EMI Filter | EMI π-type filter | Input Capacitor | |
| C1: CGA6P1X7R2A106K250AC | C2: CGA5L1X7R2A475K160AC | C6-C8: CGA6P1X7R2A106K250AC | Download Related Information |
| CMC: ACM12V-172-2PL-TL00 | L1: SPM7054VC-1R5M-D | C11-C14: CGA3E2X7R2A103K080AA | |
| C3-C4: CGA5L1X7R2A475K160AC | |||
| Adopts 3225mm/100V/10μF MLCC + 80V high-impedance CMC | Adopts 3216mm/100V/4.7μF MLCC + 80V rated power inductor | Reduced from 3225mm/100V/4.7uF x 5pcs to 3225mm/100V/10uF x 3pcs |
By configuring a multi-stage filter compatible with both common-mode and normal-mode noise, significant noise suppression in automotive 48V power supply systems was confirmed through actual measurements. Furthermore, adopting large-capacitance MLCCs for each filter and input capacitor enhances noise countermeasure effectiveness while reducing the number of components and mounting space. This enables efficient and highly reliable noise control, greatly contributing to improved EMC performance of automotive 48V power supply systems.
Product Lineup for Automotive 48V Applications
TDK offers a wide range of products for 48V lines. Each component has a specified rated voltage, so please ensure sufficient margin when using them.
Featured Products
| CGA6P1X7R2A106K250AC | Capacitance: 10uF RV: 100V / TC: X7R LxWxT: 3.2x2.5x2.5mm (1210) | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| CGA5L1X7R2A475K160AC | Capacitance: 4.7uF RV: 100V / TC: X7R LxWxT: 3.2x1.6x1.6mm (1206) | Detail |
| CGA4J1X7R2A225K125AC | Capacitance: 2.2uF RV: 100V / TC: X7R LxWxT: 2.0x1.25x1.25mm (0805) | Detail |
■MLCC Rated Voltage 100V Automotive Grade
| Series | L x W mm (EIA) | Standard Electrode | Resin Electrode | Mega Cap (Inline Type) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CGA2* | 1.0 x 0.5 (0402) | 0.001 to 0.01 uF | Detail | ||||
| CGA3* | 1.6 x 0.8 (0603) | 0.001 to 0.1 uF | Detail | 0.001 to 0.1 uF | Detail | ||
| CGA4* | 2.0 x 1.25 (0805) | 0.047 to 2.2 uF | Detail | 0.001 to 1 uF | Detail | ||
| CGA5* | 3.2 x 1.6 (1206) | 0.047 to 4.7 uF | Detail | 0.1 to 2.2 uF | Detail | ||
| CGA6* CNA6* | 3.2 x 2.5 (1210) | 1.0 to 10 uF | Detail | 0.47 to 4.7 uF | Detail | ||
| CGA8* | 4.5 x 3.2 (1812) | 1.5 to 2.2 uF | Detail | ||||
| CGA9* CKG57* CAA57* | 5.7 x 5.0 (2220) | 3.3 to 15 uF | Detail | 10 uF | Detail | 1.0 to 47 uF | Detail |
■Power Line Common Mode Choke/Filter Automotive Grade
| Part no. | Size L x W x H (mm) | Common Mode Z | DCR | Rated Current | Rated Voltage | IR |
| |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| at 100MHz | 85deg.C | 105deg.C | 125deg.C | |||||||
| (Ω) min. | (Ω) typ. | (mΩ) max. | (A) max. | (V) max. | (MΩ) max. | |||||
| ACT32P-102-2P-TL01 | 3.2x2.5x2.5 | 750 | 1000 | 150 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 80 | 10 | Detail |
| ACM55V-701-2PL-TL00 | 5.5x5.5x3.5 | 500 | 700 | 17 | 4.7 | 4 | 3.1 | 80 | 10 | Detail |
| ACM70V-701-2PL-TL00 | 7.0x6.0x3.5 | 500 | 700 | 15 | 5.5 | 4.8 | 4 | 80 | 10 | Detail |
| ACM90V-701-2PL-TL00 | 9.0x7.0x4.5 | 500 | 700 | 10 | 8 | 7 | 5 | 80 | 10 | Detail |
| ACM90V-152-2PL-TL00 | 1100 | 1500 | 16 | 5.4 | 4.5 | 3.6 | 80 | 10 | Detail | |
| ACM12V-351-2PL-TL00 | 12.0x11.0x6.0 | 240 | 350 | 2.9 | 16 | 14 | 10 | 80 | 10 | Detail |
| ACM12V-701-2PL-TL00 | 500 | 700 | 6 | 11 | 11 | 8 | 80 | 10 | Detail | |
| ACM12V-172-2PL-TL00 | 1200 | 1700 | 12 | 7 | 6 | 4.8 | 80 | 10 | Detail | |
■Power Line Inductors Automotive Grade - Recommended Products for 48V Power Systems
| Series | L x W Size (mm) | T (Max.) (mm) | Rated Voltage (V) max. | DC resistance (mΩ) typ. | Inductance (μH) | Rated Current(Isat) (A) typ. (ΔL = -30%) | Rated Current(Itemp.) (A) typ. (ΔT = 40℃) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPM7054VC* | 7.5 x 7.0 | 5.4 | 80 | 4.3 to 334 | 1.0 to 100 | 3.4 to 26.8 | 1.8 to 16.2 | Detail |
■ESD/Voltage Protection Devices Automotive Grade
Item | Chip Size mm (inch) | Operating Voltage (V) | Varistor Voltage (V) | Capacitance (pF) | Surge Current (8/20us) (A) | Energy (10/100us) (J) | ESD Durability 150pF/330Ω Contact (kV) | Operating Temp. (℃) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVRM1608C720KT750M | 1.6 x 0.8 (0603) | 53Max | 72 (64.8 to 79.2) | 75 (60 to 90) | 40 | 0.1 | ±25 | -50 to +150 | Detail |
| AVRM2012C720KT201M | 2.0 x 1.25 (0805) | 53Max | 72 (64.8 to 79.2) | 200 (160 to 240) | 100 | 0.3 | ±25 | -50 to +150 | Detail |
Summary: Noise Control for Automotive 48V Power Supply Systems and TDK’s Total Support
With the advancement of automotive 48V power supply systems, noise control has become increasingly important. Actual measurement examples have confirmed that multi-stage filters combining common mode choke coils, inductors, and large-capacitance MLCCs can significantly reduce noise across a wide frequency range. In addition, the adoption of large-capacitance MLCCs helps reduce the number of components and mounting space.
TDK offers a wide range of noise countermeasure components for automotive 48V power supply systems, as well as comprehensive technical support including EMC testing services and circuit design proposals. If you are facing challenges with noise control in automotive 48V power supply systems, TDK provides total support from optimal component selection to evaluation and verification. Please feel free to contact us to enhance the reliability and EMC performance of your automotive 48V power supply systems.