- Power Supplies, Sources and Loads >
- AC-DC Power Supplies
A. Constant current control power supplies and power supplies with a CVCC function are recommended for battery charging.
These power supplies can be found under the Constant Voltage/Constant Current (CVCC) power supply category or AC-DC Power Supplies (AC-DC Converters) > Simple Constant Current Control on the Power Supply portal site of the product information website (TDK Product Center).
However, there are cases where a power supply with an overcurrent protection function is used for battery charging.
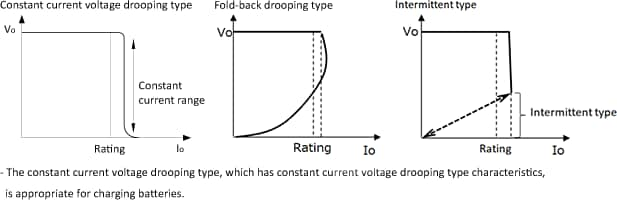
The overcurrent protection function is intended to prevent deterioration of and damage to the power supply by suppressing the current value when the power supply is overloaded and the current exceeds the rated current value. Here, operation of the current value suppression function diverts the current, and the diverted current is used for constant current to charge the battery. It should be noted that some overcurrent protection characteristics are not suitable for battery charging.
Figure 1
Caution must be exercised when selecting power supplies because other power supplies with overcurrent protection characteristics are not appropriate for charging batteries.
Furthermore, the constant current range is the state where overcurrent protection for avoiding deterioration and damage in the power supply is operating as explained above, and its use is the exceeding of the rated current stipulated in the specifications of the power supply (rated current < overcurrent protection setting current).
In this case, a substandard for changing the overcurrent protection setting current value of the power supply is needed so that the overcurrent protection setting current < the rated current.
There is also a method of controlling constant currents by connecting the external circuitry to the power supply in addition to the method explained previously where the overcurrent protection function is diverted.
This is a concrete explanation using our HWS1000 as an example (Figure 2).
Figure 2 Constant current circuitry for charging batteries when using the HWS1000
This method is an example of a constant current circuit configuration of power supplies with external controls of output voltages (PV variable functions) and always requires use at the rated power or below.
Also, be sure to use lithium-ion and other such batteries with a battery management system (BMS*). When charging and discharging are repeatedly performed, differences in the charging capacity of the individual cells occur, and if discharging occurs in this condition, overcharging can occur. Consequently, a BMS that monitors the voltage of each cell and suspends charging/discharging if a single cell over charges or over discharges should be used to ensure safety and prevent deterioration.
* A system that monitors and controls the status of battery modules (battery packs). Also referred to as a battery management unit (BMU).
Related Information