Chip NTC Thermistor Simulation
Why Do You Need This Simulation Tool?
Advantage 1: Save time and money on creating prototype boards
By pairing an NTC Thermistor with a resistor, you can achieve various temperature-voltage curves. This simulation tool can perform 10 different temperature/voltage simulations as shown in the figure on the right.
Advantage 2: Find the right thermistor for your design requirements, reducing potential issues
To use a NTC thermistor safely, you can check its own temperature rise. If self-heating exceeds the specified value within the usage temperature range, the NTC thermistor may heat up, and in the worst case, lead to a malfunction. For safe usage, please verify the recommended NTC thermistor and resistance value for each circuit by simulation in advance.
>>Failure Modes and Countermeasures in Actual Use of NTC Thermistors
Advantage 1: Save time and money on creating prototype boards
By pairing an NTC Thermistor with a resistor, you can achieve various temperature-voltage curves. This simulation tool can perform 10 different temperature/voltage simulations as shown in the figure on the right.
Advantage 2: Find the right thermistor for your design requirements, reducing potential issues
To use a NTC thermistor safely, you can check its own temperature rise. If self-heating exceeds the specified value within the usage temperature range, the NTC thermistor may heat up, and in the worst case, lead to a malfunction. For safe usage, please verify the recommended NTC thermistor and resistance value for each circuit by simulation in advance.
>>Failure Modes and Countermeasures in Actual Use of NTC Thermistors

Product Type
-
Application
- Chip Size
Conditions
- Vin / V (5V Max.) ?
- Temperature Range / ℃ ? to
- Vout / V (0<Vout<Vin) ? to
-
R1 Tolerance / %R2 Tolerance / %R3 Tolerance / %
- Temp.ppm / ppm/℃
- [Current condition]
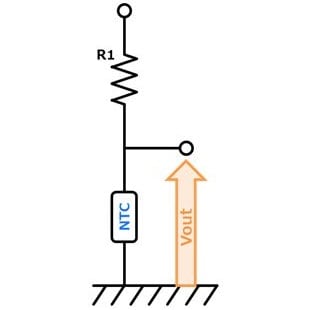
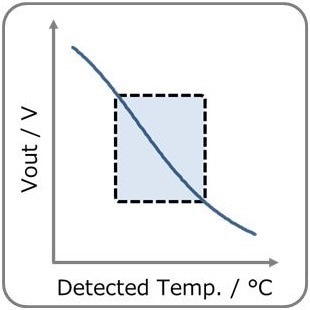
- General circuit. By dividing the voltage into a thermistor and fixed resistor, it prevents thermal runaway due to self-heating of the thermistor.
Vout decreases with temperature rise.
| Graph | Judgement ? | R25 / Ω | Part No. ? | Tolerance / % | B value [25/50°C] / K | B value [25/85°C] / K | B value [25/100°C] / K | Recommended R1/Ω |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Vout
Change settings
Temperature Rise ?
Change settings
Gain
Change settings
Vout Error
Change settings
Sensing Temp. Error
Change settings
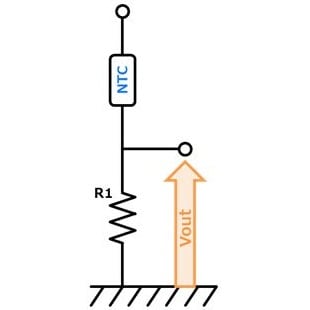
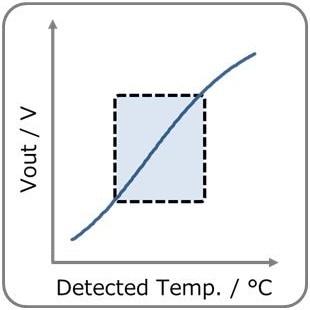
- General circuit. By dividing the voltage into a thermistor and fixed resistor, it prevents thermal runaway due to self-heating of the thermistor.
Vout increases with temperature rise.
| Graph | Judgement ? | R25 / Ω | Part No. ? | Tolerance / % | B value [25/50°C] / K | B value [25/85°C] / K | B value [25/100°C] / K | Recommended R1/Ω |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Vout
Change settings
Temperature Rise ?
Change settings
Gain
Change settings
Vout Error
Change settings
Sensing Temp. Error
Change settings
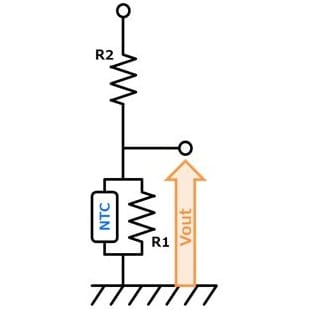
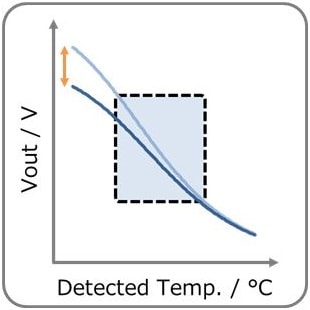
- You can adjust Vout by adjusting R1 & R2. (R1:Low temp side) Vout decreases with temperature rise. Also, self-heating of the thermistor can be reduced.
| Graph | Judgement ? | R25 / Ω | Part No. ? | Tolerance / % | B value [25/50°C] / K | B value [25/85°C] / K | B value [25/100°C] / K | Recommended R1/Ω | Recommended R2/Ω |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Vout
Change settings
Temperature Rise ?
Change settings
Gain
Change settings
Vout Error
Change settings
Sensing Temp. Error
Change settings
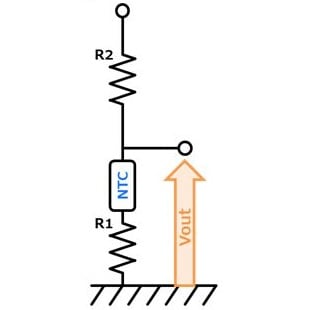
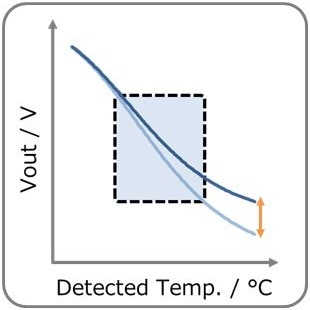
- You can adjust Vout by adjusting R1 & R2. (R1:High temp. side) Vout decreases with temperature rise. Also, self-heating of the thermistor can be reduced.
| Graph | Judgement ? | R25 / Ω | Part No. ? | Tolerance / % | B value [25/50°C] / K | B value [25/85°C] / K | B value [25/100°C] / K | Recommended R1/Ω | Recommended R2/Ω |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Vout
Change settings
Temperature Rise ?
Change settings
Gain
Change settings
Vout Error
Change settings
Sensing Temp. Error
Change settings
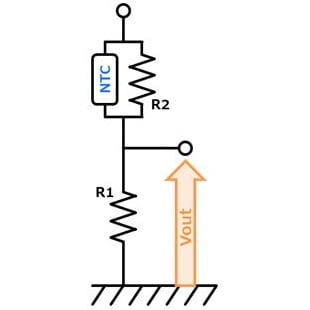
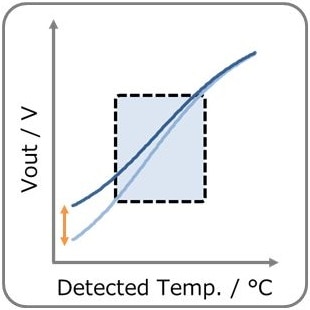
- You can adjust Vout by adjusting R1 & R2. (R2:Low temp. side) Vout increases with temperature rise. Also, self-heating of the thermistor can be reduced.
| Graph | Judgement ? | R25 / Ω | Part No. ? | Tolerance / % | B value [25/50°C] / K | B value [25/85°C] / K | B value [25/100°C] / K | Recommended R1/Ω | Recommended R2/Ω |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Vout
Change settings
Temperature Rise ?
Change settings
Gain
Change settings
Vout Error
Change settings
Sensing Temp. Error
Change settings
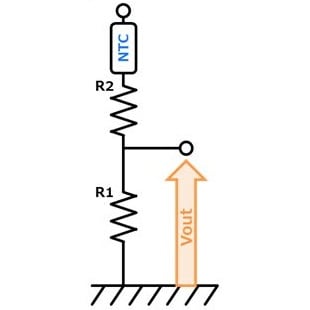
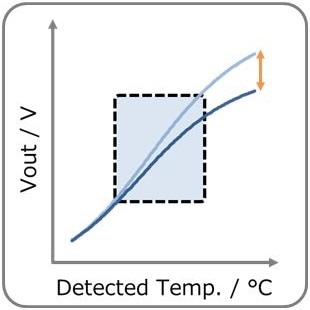
- You can adjust Vout by adjusting R1 & R2. (R2:High temp. side) Vout increases with temperature rise. Also, self-heating of the thermistor can be reduced.
| Graph | Judgement ? | R25 / Ω | Part No. ? | Tolerance / % | B value [25/50°C] / K | B value [25/85°C] / K | B value [25/100°C] / K | Recommended R1/Ω | Recommended R2/Ω |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Vout
Change settings
Temperature Rise ?
Change settings
Gain
Change settings
Vout Error
Change settings
Sensing Temp. Error
Change settings
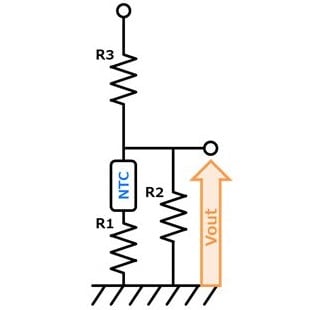
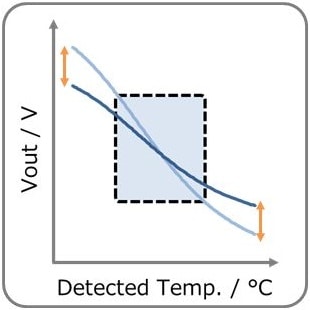
- You can adjust Vout by adjusting R1, R2 & R3. (R1:High temp. side, R2:Low temp. side) Vout decreases with temperature rise. Also, self-heating of the thermistor can be reduced.
- Depending on the conditions, the simulation may take up to one minute.
| Graph | Judgement ? | R25 / Ω | Part No. ? | Tolerance / % | B value [25/50°C] / K | B value [25/85°C] / K | B value [25/100°C] / K | Recommended R1/Ω | Recommended R2/Ω | Recommended R3/Ω |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Vout
Change settings
Temperature Rise ?
Change settings
Gain
Change settings
Vout Error
Change settings
Sensing Temp. Error
Change settings
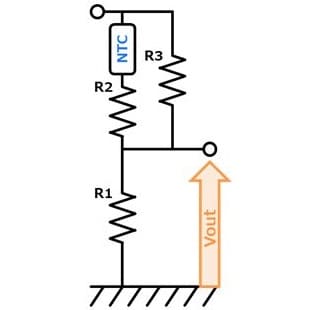
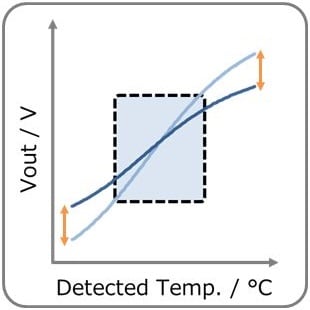
- You can adjust Vout by adjusting R1, R2 & R3. (R2:High temp. side, R3:Low temp. side) Vout increases with temperature rise. Also, self-heating of the thermistor can be reduced.
- Depending on the conditions, the simulation may take up to one minute.
| Graph | Judgement ? | R25 / Ω | Part No. ? | Tolerance / % | B value [25/50°C] / K | B value [25/85°C] / K | B value [25/100°C] / K | Recommended R1/Ω | Recommended R2/Ω | Recommended R3/Ω |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Vout
Change settings
Temperature Rise ?
Change settings
Gain
Change settings
Vout Error
Change settings
Sensing Temp. Error
Change settings
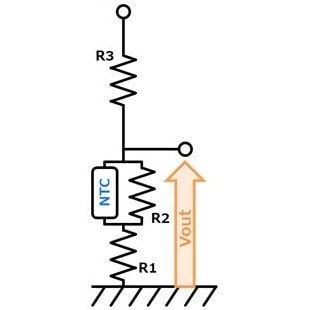
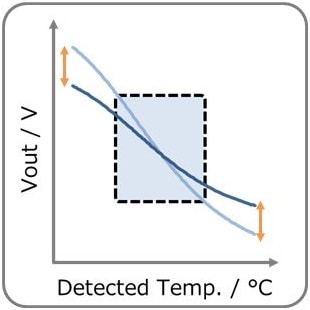
- You can adjust Vout by adjusting R1, R2 & R3. (R1:High temp. side, R2:Low temp. side) Vout decreases with temperature rise. Also, self-heating of the thermistor can be reduced.
- Depending on the conditions, the simulation may take up to one minute.
| Graph | Judgement ? | R25 / Ω | Part No. ? | Tolerance / % | B value [25/50°C] / K | B value [25/85°C] / K | B value [25/100°C] / K | Recommended R1/Ω | Recommended R2/Ω | Recommended R3/Ω |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Vout
Change settings
Temperature Rise ?
Change settings
Gain
Change settings
Vout Error
Change settings
Sensing Temp. Error
Change settings
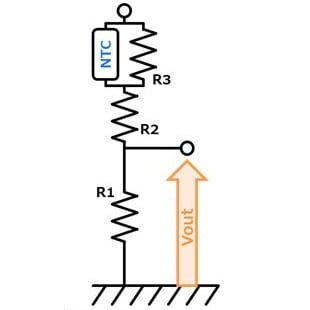
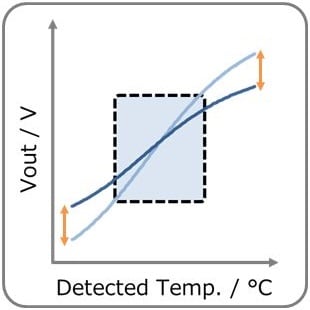
- You can adjust Vout by adjusting R1, R2 & R3. (R2:High temp. side, R3:Low temp. side) Vout increases with temperature rise. Also, self-heating of the thermistor can be reduced.
- Depending on the conditions, the simulation may take up to one minute.
| Graph | Judgement ? | R25 / Ω | Part No. ? | Tolerance / % | B value [25/50°C] / K | B value [25/85°C] / K | B value [25/100°C] / K | Recommended R1/Ω | Recommended R2/Ω | Recommended R3/Ω |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Vout
Change settings
Temperature Rise ?
Change settings
Gain
Change settings
Vout Error
Change settings
Sensing Temp. Error
Change settings

