Common Mode Chokes and Chip Varistors for 10BASE-T1S

In-vehicle Ethernet is attracting attention in automotive networks, and interfaces such as 100BASE-T1 (100Mbps) and 1000BASE-T1 (1Gbps), whose specifications are defined by the OPEN Alliance, are becoming popular. Recently, a new 10BASE-T1S (10 Mbps) has been added to this in-vehicle Ethernet, attracting a great deal of attention because of its ability to provide multi-drop connections.
This article introduces common-mode chokes and chip varistors that comply with OPEN Alliance specifications at the right time.
10Base-T1S Overview
10BASE-T1S is one of the latest IEEE Automotive Ethernet standards developed as the IEEE802.3cg standard (Table 1). The OPEN Alliance(*) is also starting to develop 10BASE-T1S-related standards that will serve as benchmarks for automotive-related manufacturers.
The data rate of this 10BASE-T1S is 10 Mbps slower than the existing 100BASE-T1 (100 Mbps) and 1000BASE-T1 (1 Gbps), but one major difference is that it allows multi-drop connections. In the conventional 100BASE-T1 and 1000BASE-T1 connection methods, only Peer to Peer connections (P2P connections), in which communicating ECUs are connected one-to-one, were possible. In contrast, 10BASE-T1S supports multi-drop connections that allow multiple nodes on a single line, making it possible to create a CAN-like network using the Ethernet protocol (Figure 1).
However, multi-drop connections have multiple nodes conneceted on a single line, which imposes stricter constraints on the line-to-line parasitic capacitance required of electronic components than P2P connections. 10BASE-T1S is no exception to this. In fact, the line-to-line parasitic capacitance required for common-mode chokes (CMCs) for EMC countermeasures and antistatic components (chip varistors) are strictly specified by the OPEN Alliance, so care must be taken when selecting electronic components for use in 10BASE-T1S.
TDK CMCs and varistors conform to the CMC specification (**) and ESD component specification (***) defined by the OPEN Alliance, respectively, and can be used without problems in 10BASE-T1S. From the next section, we will introduce the CMC and ESD components for this 10BASE-T1S.
* Open Alliance (One-Pair Ether-Net Alliance SIG) : An industry organization established to formulate standards and promote the spread of automotive Ethernet.
** EMC Test Specification for 10BASE-1S CMC
*** EMC Test Specification for 10BASE-1S ESD Suppression Devices
| 10BASE-T1 | 100BASE-T1 | 1000BASE-T1 | Multi-Gig BASE-T1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IEEE | IEEE802.3cg | IEEE802.3bw | IEEE802.3bp | IEEE802.3ch |
| Transmission Speed | 10Mbps | 100Mbps | 1Gbps | 2.5/5/10Gbps |
| Coding | 4B/5B (DME)*2 | PAM3 | PAM3 | PAM4 |
| Communication Method | Half-duplex transmission Full-duplex transmission (optional) |
Full duplex transmission | Full duplex transmission | Full duplex transmission |
| Topology | Peer to Peer Multidrop |
Peer to Peer | Peer to Peer | Peer to Peer |
*2:DME: Differential Manchester Encoding

10Base-T1S recommended components (common mode choke/filter)
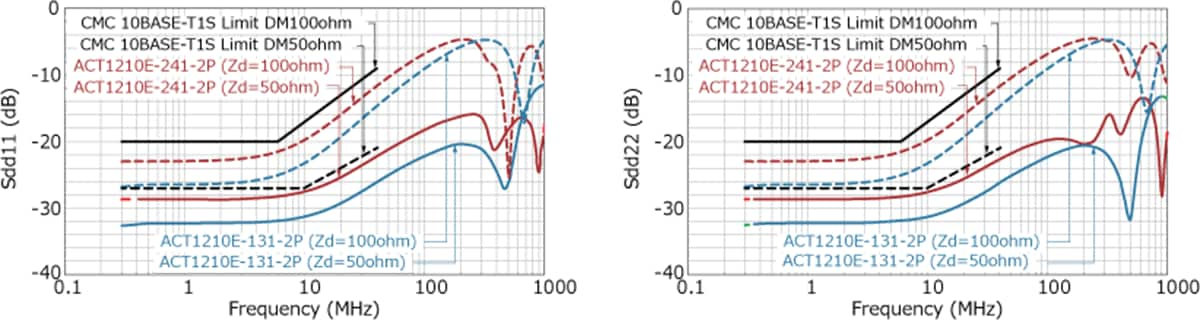
Since 10BASE-T1S is a multi-drop connection without a switch, when many ECUs are connected on a single line, reflections due to the length of the wire harness and branches and the capacitance component of the ECUs become large, and ringing in the signal waveform and other effects on communication quality are likely to occur. Therefore, CMCs for EMC must have as low parasitic capacitance as possible.
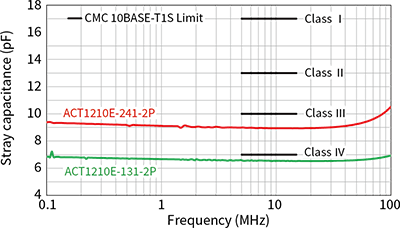
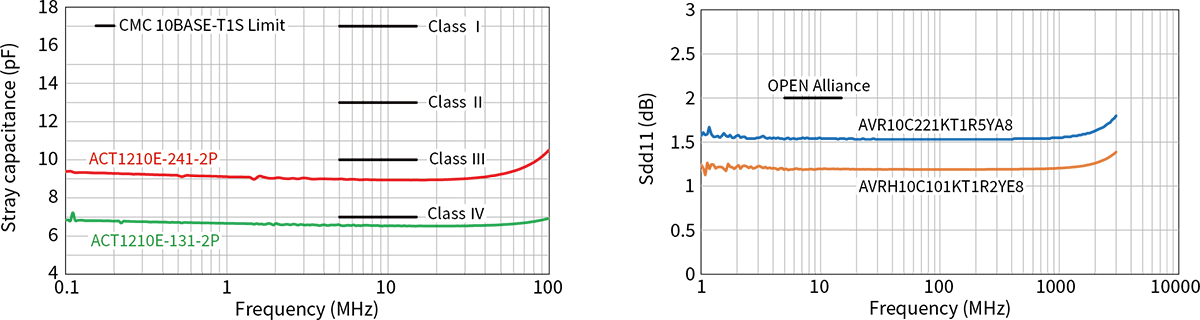
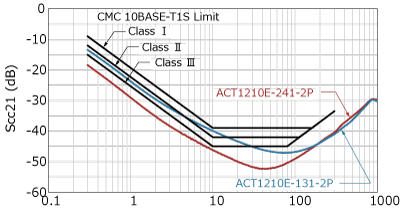
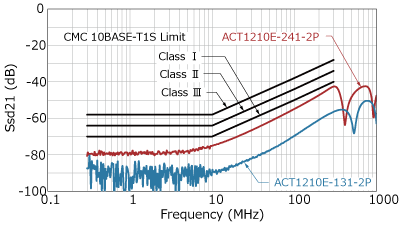
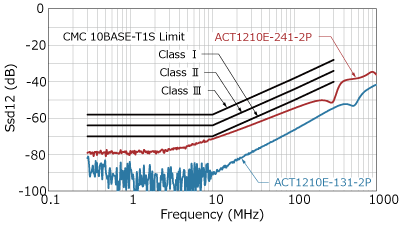
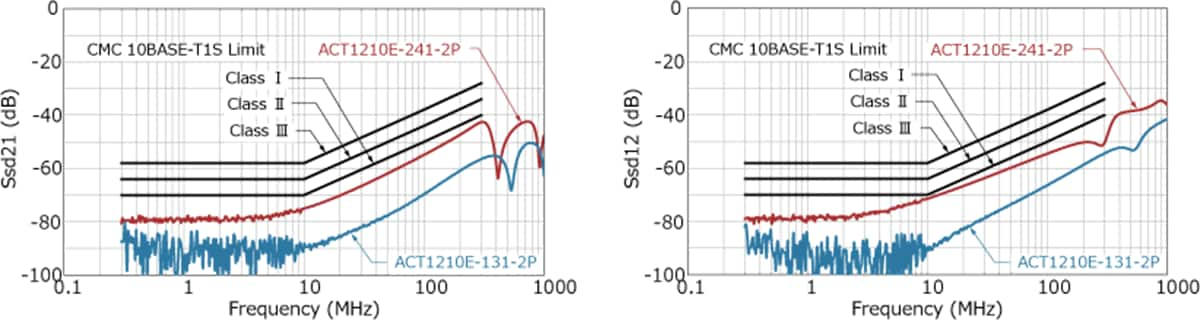
The specifications for CMC components are defined by the OPEN Alliance “10BASE-T1S EMC Test Specificaton for Common Mode Chocks”, in which parasitic capacitance is classified from Class I (17pF or less) to Class IV (7pF or less). The ACT1210E-131-2P-TL00 is the industry's first CMC product to meet the most stringent Class IV requirements.
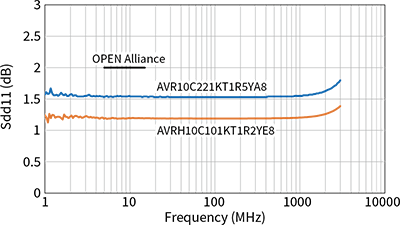
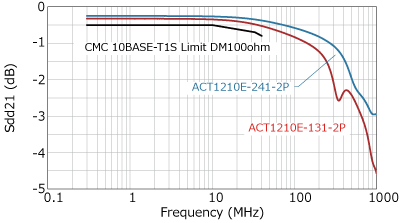
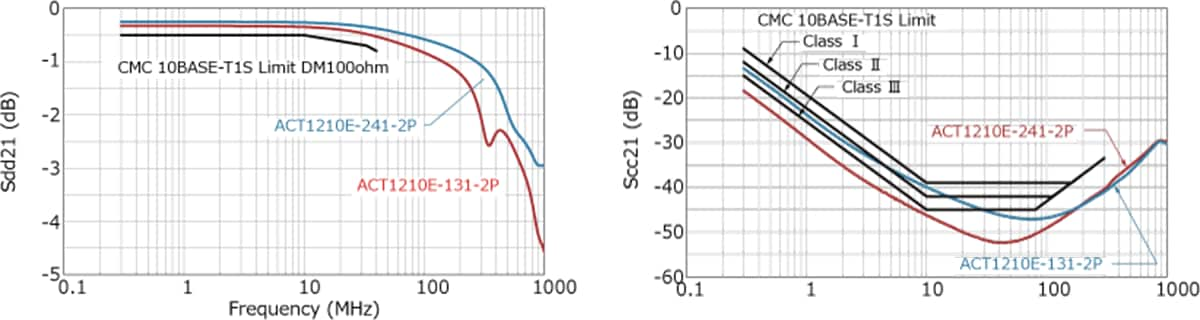
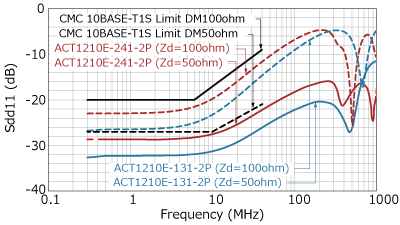
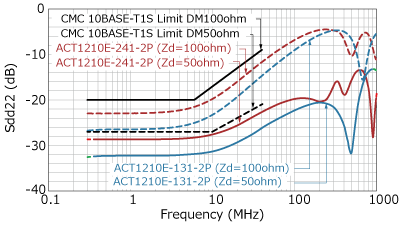
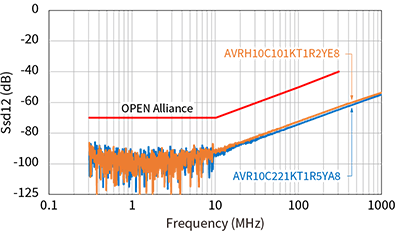
In addition to parasitic capacitance, recommended values are also specified for S parameters such as insertion loss, return loss, and mode conversion. Mode conversion means that the differential mode, which is the communication signal, and the common mode, which is the noise, are converted into each other's conduction mode. Such mode conversion can cause the ECU to emit noise or malfunction due to poor noise immunity.
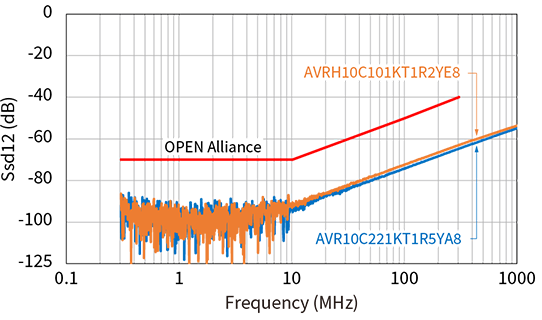
As shown in the graph below, TDK CMCs have excellent mode conversion characteristics.
| Product No. | Common Mode Inductance μH(Typ.) @100kHz |
Parasitic Capacitance pF(Max.) |
DC resistance Ω(Max.) |
Rated Current mA(Max.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACT1210E-241-2P-TL00 | 240 | 10 | 4.1 | 70 |
| ACT1210E-131-2P-TL00 | 130 | 7 | 2.9 | 70 |
10Base-T1S recommended components (chip varistors/ceramic transient voltage suppressors)
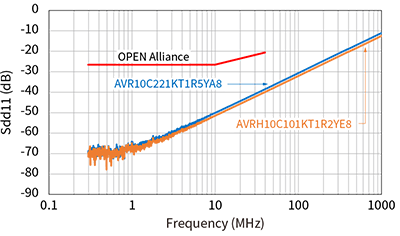
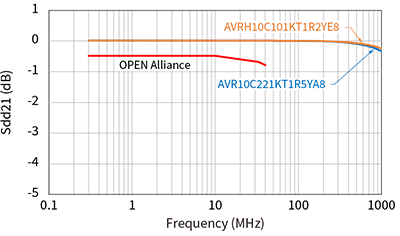
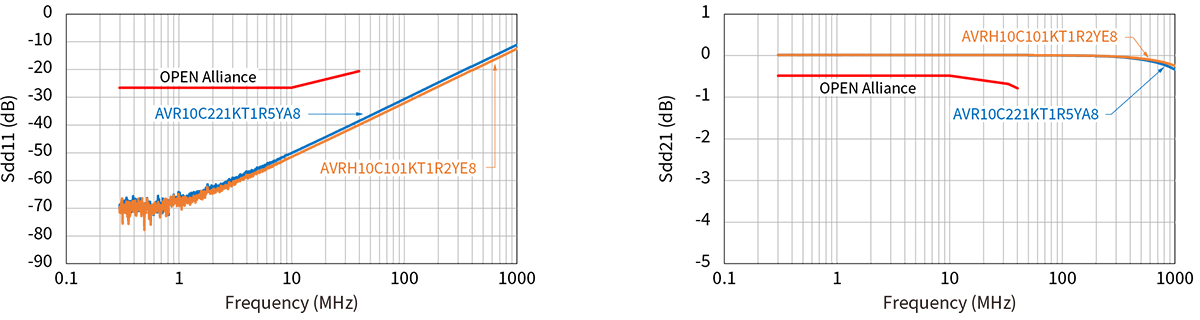
The same stringent specifications are required for ESD countermeasure components as for common mode choke coils. The 10BASE-T1S specification by the OPEN Alliance for ESD countermeasure components also strictly specifies line-to-line capacitance for anti-ESD components. As specific values, the capacitance values are as small as 1 pF or less as line-to-line capacitance, or 2 pF or less when replaced with capacitance on one of the lines. As shown in Table 3, TDK's ESD countermeasure components, the chip varistor, meets this standard value, enabling ESD countermeasures in 10BASE-T1S without worrying about capacitance.
In addition, automotive Ethernet requires products with narrower capacitance tolerances than general ESD countermeasure components. The recommended lineup for 10BASE-T1S has a capacitance tolerance of ±0.13 pF, which enables ECU designs with high immunity with minimal impact on communication quality and mode conversion characteristics.
TDK chip varistors also have high ESD protection performance and comply with the AEC-Q200 automotive reliability standard, making TDK chip varistors an excellent total balance as ESD protection devices for 10BASE-T1S.
| Product No. | L x W Dimensions mm |
Varistor Voltage V(Nom.)@1mA |
Capacitance pF |
ESD Resistance IEC61000-4-2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVRH10C101KT1R2YE8 | 1.0×0.5 EIA0402 |
110(100 to 120) | 1.23(1.1 to 1.36) | 8kV |
| AVRH10C221KT1R5YA8 | 1.0×0.5 EIA0402 |
220(198 to 242) | 1.5(1.37 to 1.63) | 25kV |
Parasitic capacitance and S-parameters of recommended components
As described above, the OPEN Alliance has defined standards for parasitic capacitance and S-parameters in the 10BASE-T1S standard. Since there are standardized lines classified by each characteristic, it is possible to select parts that meet the standard according to the usage conditions.
Below are the characteristics and specification lines for each recommended component.
Parasitic capacitance
Summary
The in-vehicle networks that connect ECUs and various devices in next-generation vehicles that are designed for fully automated driving are attracting a great deal of attention. Automotive Ethernet has standards for each different data rate. In addition to the 10Base-T1S introduced in this article, TDK offers common-mode chokes and chip varistors for each standard.