MLCC Solutions for Data Center (AI Server) Power Systems

Power Trends in Data Centers in the AI era
Source: JST Low Carbon Society Strategy Cente
"The Impact of the Information Society on Energy Consumption (Vol.4)"
(LCS-FY2021-PP-01). Prepared by TDK."
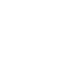
Figure 1. Current and Projected
Total Power Consumption of Data Centers
With the rapid spread of AI in recent years, server power consumption in data centers has increased dramatically. Accordingly, the importance of high-efficiency, high-power-capacity power supplies (PSUs) to support stable server operation has grown.
Moreover, advances in server cooling methods and higher integration demand strong space savings on PCBs inside server racks. As a result, passive components used in PSUs must be high-performance, compact and low-profile, and reducing PCB footprint is a major challenge.
We offer a lineup of high-voltage, high-performance capacitors and other solutions that contribute to high-efficiency power designs for data centers to meet the needs for higher power and higher density in PSUs.
Power System Architecture of Data Centers
In server power systems, a typical power chain is UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) → PSU (Vac → 48V etc.) → IBC (48V → 12V etc.) → VRM (conversion to CPU/GPU voltages). At each stage, high efficiency, low emissions, low ripple, heat tolerance, and long-term reliability are strongly required.
In environments with increasing density and output, reducing losses and managing heat at the PSU stage and improving power transmission efficiency at the IBC stage are key design considerations.
In addition to offering MLCCs rated for 100V and 450V and above, we provide MLCC configuration proposal tools and thermal design simulation services to help solve customer challenges.
- UPS: Uninterruptible Power Supply
- PSU: Power Supply Unit
- IBC: Intermediate Bus Converter
- VRM: Voltage Regulator Module
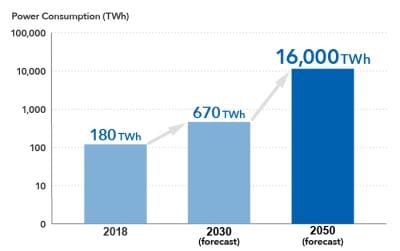
Power-performance Trends of PSUs for Data Centers
Figure 3. PSU Power Trend (TDK Estimate)
- Increase in output power: Designs are shifting from the conventional kilowatt-class to 6–12 kW and above. Higher output increases voltage and current stress on components.
- Evolution of topologies: In both PFC and DCDC stages, there is a trend toward multilevel and parallel architectures to reduce losses and distribute heat.
- Changes in component requirements: MLCCs demand higher voltage ratings, lower ESR, and higher reliability.
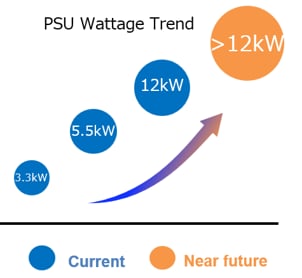
Changes in Circuit Topology for Increased PSU Power - DC/DC
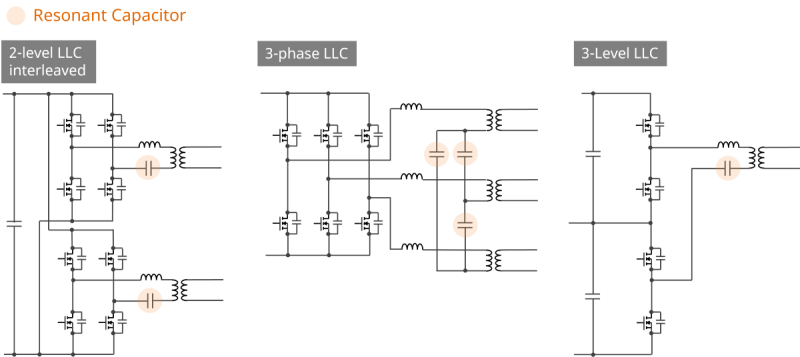
LLC resonant converters are the main topology for the PSU DC/DC stage because they achieve low switching losses and high efficiency.
For higher power, phase-parallel (interleaved) designs and series/parallel power block configurations are adopted to distribute current and heat while expanding power capacity.
- Role of MLCCs: Use high-voltage and low-loss Class 1 C0G MLCCs for the LLC resonance capacitor circuits.
- MLCC configuration proposal tool: We provide a tool to propose series/parallel MLCC configurations based on high-voltage Class 1 products and driving conditions.
| Resonant Cap. (Class1) Mid/ High Voltage Series | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1250V | C3225C0G3B103J (3.2 x 2.5mm/0.01uF) | Detail |
| 1000V | C3225C0G3A223J (3.2 x 2.5mm/0.022uF) | |
| 630V | C3225C0G2J333J (3.2 x 2.5mm/0.033uF) | |
Changes in Circuit Topology for Increased PSU Power - PFC
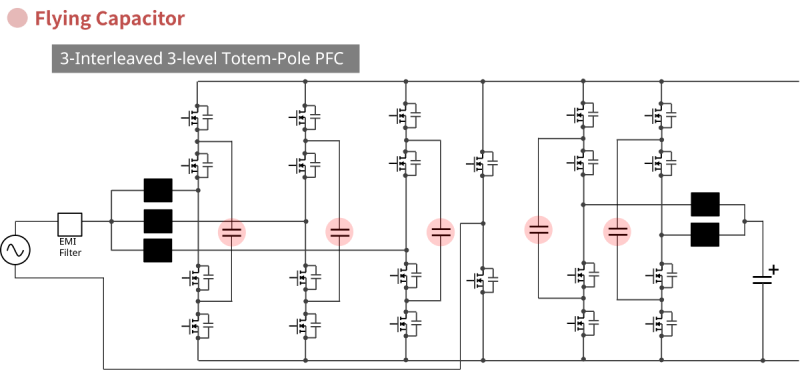
For very large power levels, circuit topologies employing flying capacitors are being considered.
Background of flying capacitor adoption: Creating intermediate potentials reduces voltage stress on semiconductors, enabling lower switching losses and lower component ratings. In three-level configurations, the applied voltage across flying capacitors is often ideally half of the DC bus, so MLCCs with 450V ratings are useful.
| Flying Capacitor Mid/ High Voltage Series | ||
|---|---|---|
| 450V | C5750X6S2W225K (~105℃) (5.7 x 5.0mm/2.2uF) | Detail |
| C5750X7T2W105K (~125℃) (5.7 x 5.0mm/1.0uF) | ||
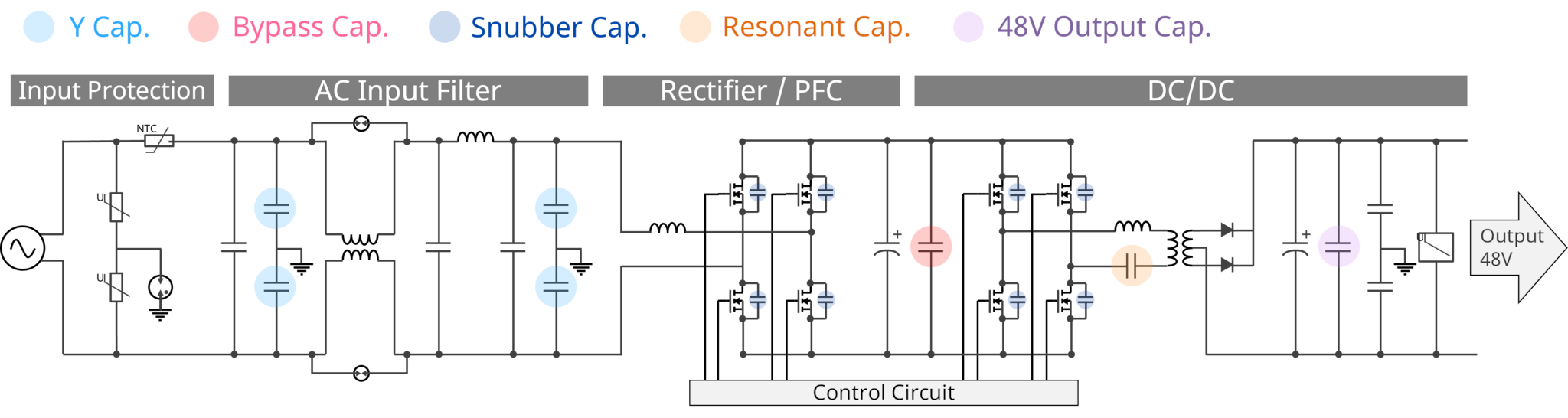
MLCC Lineup for PSU (Vac → 48V)
Introduction of MLCC products commonly used in typical PSUs. Recommended parts by application are as follows:
● Y cap.: For EMI filters, compliant with safety standard Y2 class.
● Bypass Cap.: High-voltage MLCCs rated 630V and above; used in parallel with large electrolytic capacitors to reduce ripple.
● Snubber cap.: High-voltage Class 1 MLCCs with excellent surge tolerance.
● Resonant cap.: High-voltage Class 1 MLCCs optimized for resonance.
● 48V Output Cap.: Large-capacitance MLCC with 100V and 75V ratings to reduce part count.
Featured Products
R.V. = Rated Voltage
| Y Cap. CS Series (Safety Certified Y2) | Bypass / Snubber Cap. (R.V.630V) Mid / High Voltage Series. | Resonant Cap. (Class1) Mid / High Voltage Series | 48V Output Cap. (R.V.75V~100V) Mid Voltage Series | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y2 300Vac | 4.7nF(2.2nF – 10nF) | Filtering 630V | C3225X7T2J154K (3.2 x 2.5mm/0.15uF) | 1250V | C3225C0G3B103J (3.2 x 2.5mm/0.01uF) | 100V | C3225X7R2A106K (3.2 x 2.5mm/10uF) |
| Detail | C3225X7T2J104K (3.2 x 2.5mm/0.1uF) | 1000V | C3225C0G3A223J (3.2 x 2.5mm/0.022uF) | C3216X7R2A475K (3.2 x 1.6mm/4.7uF) | |||
| C3216X7T2J473K (3.2 x 1.6mm/0.047uF) | 630V | C3225C0G2J333J (3.2 x 2.5mm/0.033uF) | C2012X7R2A225K (2.0 x 1.25mm/2.2uF) | ||||
| Detail | Detail | Detail | |||||
| Snubber 630V | 220pF to 2.2nF | 75V | C3225X7R1N106K (3.2 x 2.5mm/10uF) | ||||
| Detail | Detail | ||||||
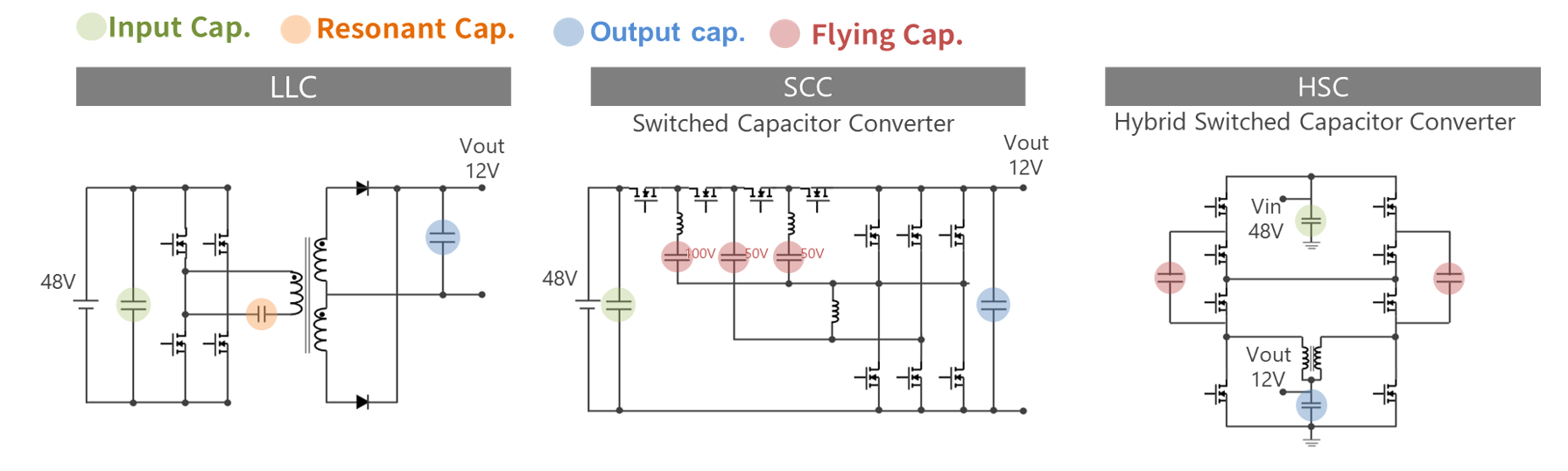
MLCC Lineup for IBC (48V → 12V, etc.)
For IBCs (48V → 12V), in addition to traditional LLC circuits, high efficiency and high density across a wide input range are required. One solution is the SCC (Switched Capacitor Converter).
● Flying Capacitor : Advantages of Using MLCCs
*High capacitance density: allows large capacitance in a small area.
*Low ESR/low ESL: robust against high-frequency ripple and switching transients, beneficial for suppressing heat generation.
*Large numbers in parallel: distribute current and thermal load per part.
For traditional LLC circuits, we can provide resonant capacitors and input capacitors with 100V ratings, and output capacitors in the 16V–25V rating range, covering the necessary lineup.
Featured Products
R.V. = Rated Voltage
| Resonant Cap. (Class1) Mid/ General Voltage Series | Input Cap. (R.V.75V~100V) Mid / General Voltage Series | Flying Cap. (R.V.50V) General Voltage Series | Output Cap. (R.V.16~25V) General Voltage Series | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100V | C3216C0G2A104J (3.2 x 1.6mm/0.1uF) | 100V | C3225X7R2A106K (3.2 x 2.5mm/10uF) | 50V | C3225X7R1H106K (3.2 x 2.5mm/10uF) | 25V | C3225X7R1E226M (3.2 x 2.5mm/22uF) |
| 50V | C3216C0G1H104J (3.2 x 1.6mm/0.1uF) | C3216X7R2A475K (3.2 x 1.6mm/4.7uF) | C3216X7R1H106K (3.2 x 1.6mm/10uF) | C3216X7R1E106K (3.2 x 1.6mm/10uF) | |||
| C2012C0G1H333J (2.0 x 1.25mm/0.033uF) | C3216X6S2A106K (3.2 x 1.6mm/10uF) | C2012X7R1H475K (2.0 x 1.25mm/4.7uF) | 16V | C3225X7R1C226M (3.2 x 2.5mm/22uF) | |||
| Detail | 75V | C3225X7R1N106K (3.2 x 2.5mm/10uF) | Detail | C3216X7R1C106K (3.2 x 1.6mm/10uF) | |||
| Detail | Detail | ||||||
Summary
This article introduced the latest PSU trends for data center power systems and MLCC product families for PSU/IBC applications. For PSUs moving toward higher efficiency and higher density, choosing the appropriate products such as high-voltage MLCCs and 100V-rated parts for IBC applications is essential. TDK supports improved design quality and reliability for PSU/IBC with a broad MLCC lineup and design support tools including MLCC configuration proposal tools. We will continue to provide solutions that respond to diversifying needs.