Power Inductors VLS Series
Product Overview
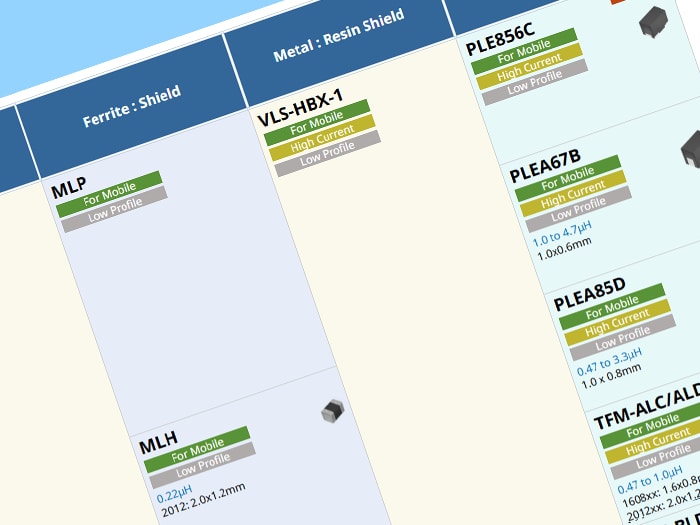
The VLS-HBX/HBU wire-wound type inductors, use metallic magnetic materials for the core, while the VLS-CX/CX-H/CZ-HE series and VLS-EX/EX-H/EX-D series utilize ferrite materials. In all series, leakage flux is reduced by covering the winding portion with resin containing magnetic material.
Series | ||||||||
Product Overview | Wire-wound and Magnetic Shield Type Inductor Use metallic materials | Wire-wound and Optimized core shape from | Wire-wound and Uses optimal structural design to | |||||
Features | Supports high current | Uses ferrite materials to achieve | Utilizes metallic terminals, | |||||
Applications | ||||||||
Smartphones | Boost | Smartphone | Automotive equipment | Automotive equipment | TVs, | Automotive equipment | Automotive equipment | |
Product Structure
The structure of the VLS series can be largely divided into two. The VLS-HBX/HBU series and the VLS-CX/CX-H/CZ-HE series is smaller and thinner due to the terminal electrode structure. The VLS-EX/EX-H/EX-D series has metal terminals, and classified as medium-sized products of 5mm and 6mm square.
Product Features
Figure 3 shows the features of each VLS series. The VLS-HBU series achieves high withstanding voltage by coating the metal core. The VLS-CX-H/EX-H series, VLS-CZ-HE series, and VLS-EX-D series are automotive products with an operating temperature range of 125°C, 135℃ and 150°C, respectively.
Series | ||||||||
Appearance | ||||||||
Core | Metal | Metal + coating | Ferrite | |||||
Magnetic materials for outer resin | Metal | Ferrite | Metal | |||||
Applications | ||||||||
Operating temperature range: | -40 to 105℃ | -40 to 125℃ | -40 to 135℃ | -40 to 105℃ | -40 to 125℃ | -40 to 150℃ | ||
Features | Supports high current | High withstand voltage due to metal core coating | High withstand voltage due to ferrite core | Compact, low profile due to silver electrode structure | Wide bandwidth and high impedance | Wide lineup from 0.47 to 680uH | Medium size 5-6mm using metal terminals | Supports high current due to metallic exterior resin |
| Size | 2016 to 4mm square | 252010,252012 | 2016 to 4mm square | 3 to 4mm square | 3mm square | 5 to 6mm square | 5 to 6mm square | 5mm square |
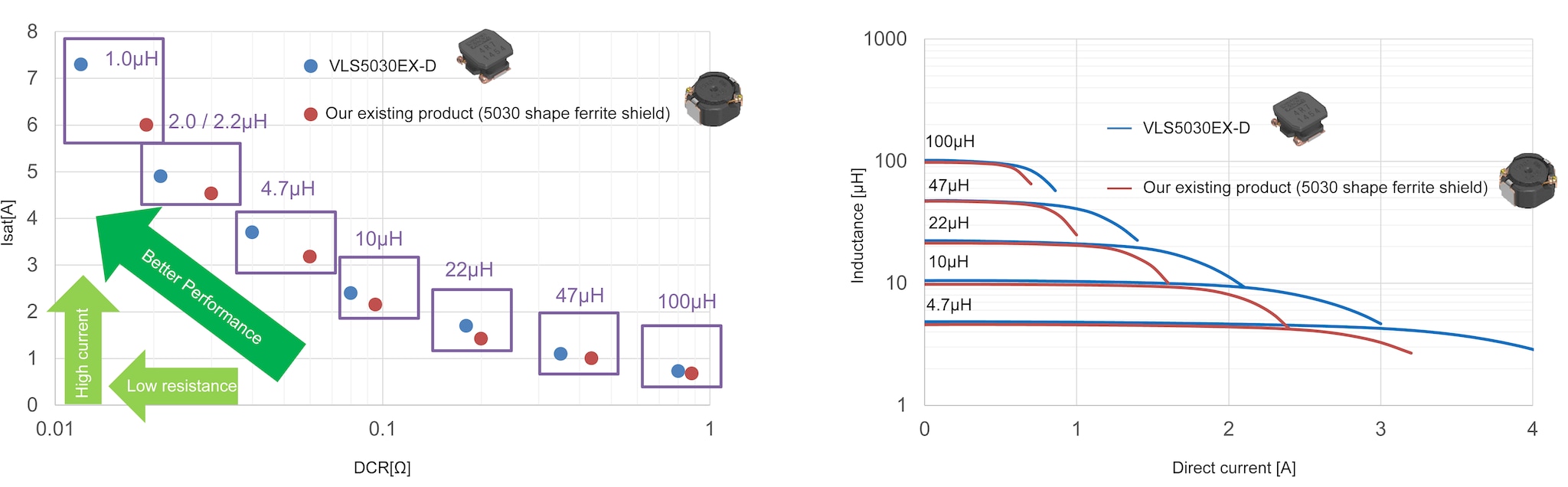
For automotive specifications, we have added the VLS5030EX-D series to our lineup, the first of our resin-shielded inductors that can be used in high-temperature environments up to 150°C. By adopting a resin shield structure that maximizes the core volume and using metallic magnetic materials for the resin shield function, we have achieved superior electrical characteristics compared to our ferrite shield coils of the same size. Achieves excellent electrical characteristics.
Applications
The optimal VLS series for each application circuit is shown in Figure 5.
The VLS-HBU series is suitable for boost-type DC-DC converters.
The automotive grade VLS-EX-D series can be used in high-temperature environments up to 150°C, including engine rooms.
Applications | DC-DC Converter (Buck Type) | DC-DC Converter (Boost Type) | |||
Product Series | VLS-HBX VLS-CX VLS-EX |
| VLS-HBU | ||
|
| VLS-CX-H (~125℃) VLS-EX-H (~125℃) VLS-CZ-HE (~135℃) VLS-EX-D (~150℃) | ||||
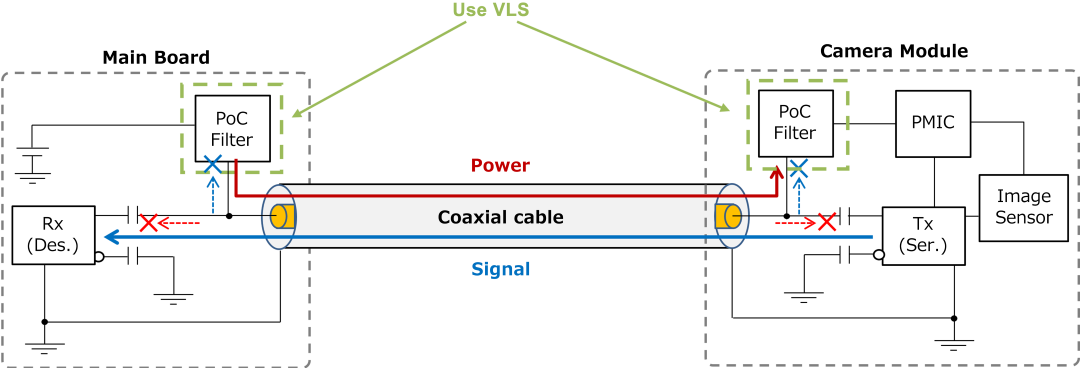
In recent years, the use of Power over Coax (PoC), which overlays signals and power on a single coaxial cable between the camera and the ECU to reduce vehicle weight and material cost, has been increasing. The VLS-CX-H/CZ-HE/EX-H/EX-D series can also be used as a PoC filter to separate the necessary signals and power in PoC circuits.
Product List
The product list for each series and shape is shown in Figure 7. Clicking on the series name allows you to view detailed information and purchase samples.
Size (mm) | Height (mm) | VLS-HBX | VLS-HBU | VLS-CX | VLS-CX-H | VLS-CZ-HE | VLS-EX | VLS-EX-H | VLS-EX-D |
2.0×1.6 | 1.0 Max. |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
1.2 Max. |
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
2.5×2.0 | 1.0 Max. |
|
|
|
|
| |||
1.2 Max. |
|
|
|
|
| ||||
3.0×3.0 | 1.0 Max. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
1.2 Max. |
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
1.5 Max. |
|
|
|
|
| ||||
4.0×4.0 | 1.2 Max. |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
1.5 Max. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
2.0 Max. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
5.0×5.0 | 3.0 Max. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
4.5 Max. |
|
|
|
|
| ||||
6.0×6.0 | 4.5 Max. |
|
|
|
|
|
What are power inductors?
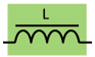
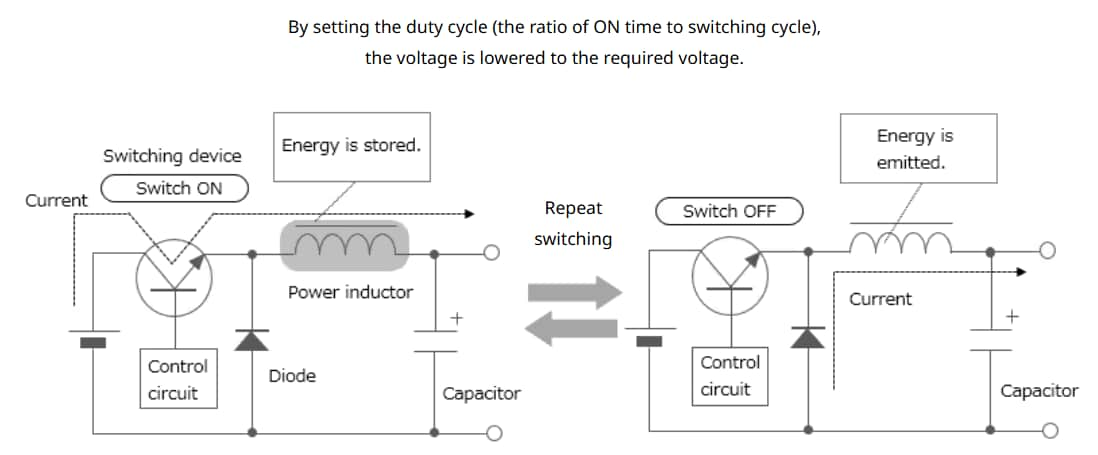
A power inductor is an inductor used in power circuits such as DC-DC converters, and is sometimes called a power coil or a power choke. Inductors have the property of storing energy through self-induction, and DC-DC converters, such as chopper-type converters, use a combination of this inductor and switching elements to convert voltage. (Refer to Figure 8).
Inductors are classified into multilayer, thin-film, and wire-wound types according to their construction methods. The wire-wound type, which can carry large currents, is the mainstream for power inductors This type can be integrated with a variety of products that have either ferrite or soft magnetic metal cores. In recent years, smaller and thinner multilayer and thin-film types are also becoming capable of handling large currents.