Compact Common Mode Filters for 20 Gbps High-Speed Differential Signaling: TCM06U Series

The TCM06U series, a compact common mode filter, is introduced as an optimal solution for noise suppression in high-speed differential signaling.
Types and Characteristics of High-Speed Differential Signaling
The exchange of large volumes of data and video signals within digital devices or between devices typically utilizes a communication method known as differential signaling.
Differential signaling involves sending two digital signals with opposite phases and extracting the difference as the received signal. This method cancels out common-mode noise, which is in-phase, making it highly resistant to noise. Additionally, the low signal voltage allows for easier high-frequency operation, enabling high-speed transmission.
High-speed communication using differential signaling includes various standards, such as widely used interfaces like USB and HDMI, as well as those used for internal device connections.
| Classification | Types of Standards | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| External Interface | USB, HDMI, Display Port, Thunderbolt, etc. | Used for connections between devices, primarily involving user plug-and-play of cables |
| Internal Interface | mipi, LVDS, etc. | Used for connections within a device, not visible to the user |
Increasing Speeds of USB Standards
Next, we discuss the trend toward higher speeds in high-speed differential signaling. Below is the trend in signal speeds for USB standards across generations.
Since the establishment of the USB 2.0 standard in 2000, USB has gained widespread adoption as an interface for connecting computers and peripheral devices. With each subsequent generation, transmission speeds have increased significantly. Many modern electronic devices, including computers, now support USB4, which offers approximately 100 times the transmission speed of USB 2.0. Furthermore, the latest USB4 Version 2 standard, established in 2022, enables transmission speeds of up to 120 Gbps over a single cable. Devices supporting this standard are expected to be released in the near future.
| Maximum Transmission Speed | Maximum Number of Lanes | Transmission Speed per Lane | |
|---|---|---|---|
| USB4 | 40Gbps | 2 | 20Gbps |
| USB 3.2 Gen2 | 20Gbps | 2 | 10Gbps |
| USB 3.2 Gen1 | 10Gbps | 2 | 5Gbps |
| USB2.0 | 480Mbps | 1 | 480Mbps |
Role of Common Mode Filters
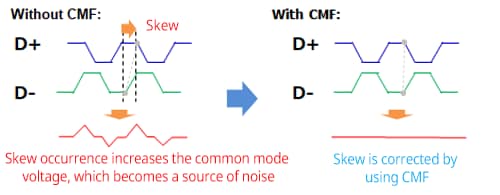
Although differential signaling is highly noise-resistant, physical and electrical mismatches in transmission lines can cause signal phase misalignment, known as skew. When skew occurs, the ability to cancel common-mode noise is reduced, leading to the generation of high-frequency noise corresponding to the signal frequency. Such high-frequency noise can degrade the reception sensitivity of RF signals, such as Wi-Fi, making countermeasures necessary.
A common mode filter incorporates two magnetically coupled inductors. It suppresses common-mode noise by generating an induced electromotive force that opposes changes in magnetic flux caused by common-mode noise, thereby correcting skew.
On the other hand, since differential signals operate in differential mode, the magnetic flux generated between the two inductors cancels out, allowing the signal current to be transmitted without interference.
As described above, a common mode filter only suppresses common-mode noise while allowing differential signals to pass through unaffected.
Skew Correction
Skew ➡ Signal phase misalignment between D+/D-
Signal Phase Misalignment Due to Physical and Electrical Mismatches in Signal Lines
In such cases, countermeasures such as filters are required.
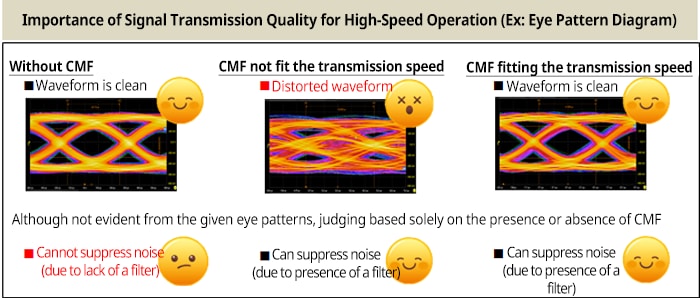
Impact of Common Mode Filters on Signal Quality
As described above, common mode filters are well-suited for noise suppression in differential signaling. However, due to the inherent properties of inductors, insertion loss increases as the signal frequency rises, which can suppress the transmission signal. Therefore, when selecting a common mode filter, it is essential to consider not only its noise suppression capability but also its ability to maintain transmission quality according to the signal frequency.
Features of the TCM06U Series
The TCM06U series offers high noise suppression performance while providing improved support for high-frequency signals compared to conventional products.
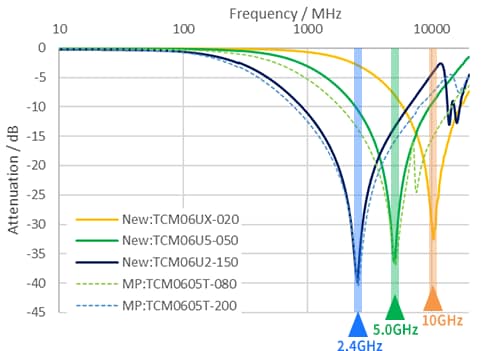
- The common mode attenuation characteristics, which serve as an indicator of common-mode noise suppression performance, achieve attenuation of 30 dB or more at each target frequency.
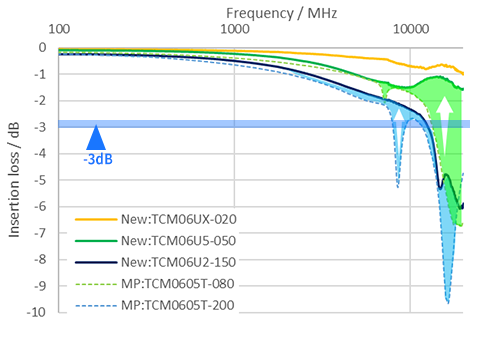
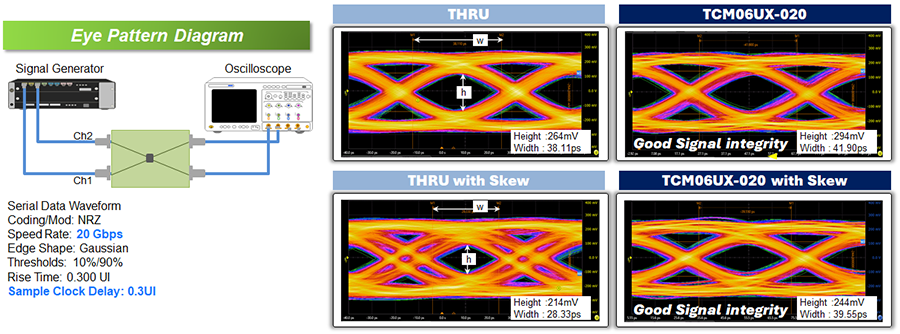
- In terms of differential mode insertion loss, a key indicator for maintaining signal quality, significant reduction in loss has been achieved compared to conventional products (TCM0605T series). This enables support for high-speed signals up to 20 Gbps, equivalent to one lane of USB4. Notably, the TCM06UX-020-2P achieves ultra-low insertion loss of approximately -1 dB at 20 GHz.
It has been confirmed through 20 Gbps high-speed transmission tests, that the signal waveform remains unaffected. Furthermore, even in waveforms with intentionally introduced skew, it has been verified that the use of common mode filters provide effective skew correction.
Common Mode Attenuation Characteristics (Scc21)
Differential Mode Insertion Loss Characteristics (Sdd21)
Summary
As described above, the TCM06U series is an optimal solution for noise suppression in high-speed differential signaling, such as USB4, while maintaining signal quality.
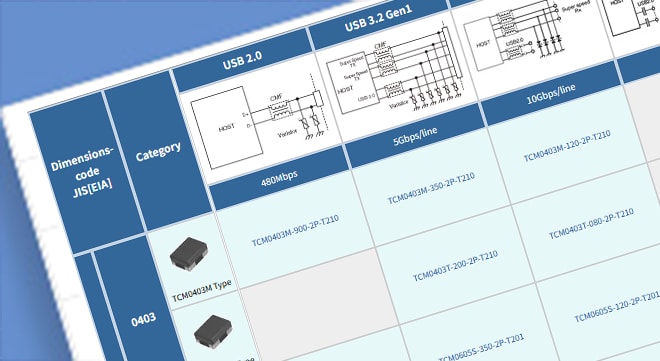
In addition to the TCM06U series introduced here, TDK offers a range of products tailored to various interfaces, including the industry's smallest 0403-sized components. TDK also provides ESD protection components designed for use alongside common mode filters in high-speed differential signaling circuits.
For technical articles on ESD protection components and recommended component combinations for specific interfaces, please refer to the link below.